The late embracing of the Indo-Pacific concept by the United States further supports the position that it is being employed as a strategic instrument to counter a rising power and a potential challenger to its global quasi-hegemonic power position.
Based on a consideration of capabilities, the United States is currently the only country that can be described as a potential global hegemon. Certainly, there are a number of other countries that have the potential, based on their capabilities, of being candidates to become regional hegemons. Notably, China is among them, but Japan, India, and Brazil are also potential candidates, though their individual capacities vary widely and one could argue, based on capacities, that China takes the lead among them. With the implication that China becomes the main target of the de facto global hegemon, the other potential contenders must be kept in sight, as well. While most recent academic and non-academic discussions about global power transfer are focusing on rising countries, on potential challengers to the existing global hegemon, China in particular, a focus on how the existing quasi-global hegemon, the United States, is reacting to challenges to its dominance, to preserve its leading position and influence, seems almost completely missing. This lack of emphasis constitutes a rather critical issue, because when we focus on global or regional power competition, what should be of interest to analysts is not only the behaviour and strategy of a rising county, i.e., a potential challenger to an existing hegemon, but also to analyse the response of the existing hegemon, as well. After all, when it comes to issues of global and regional stability, the actions of both the existing hegemon and the potential challenger must be taken into account.
There is no doubt that an existing hegemon does not just ‘sit back’ and watch when its influence is challenged by a new contender for power. Even a declining hegemon will try to challenge a rising power contender, consequently, the potential for instability within the international system arises not only from a rising power but also from the actions of the country which possesses a quasi-hegemonic position, trying to defend its power position. In one of his earlier and most influential works, Mearsheimer (2001) points out that great powers always aim to maximise their share of power and are in constant competition with other power contenders, with the aim of maximising their own power. Therefore, the rise of a new competitor occurs in a dynamic context between the established and the rising hegemon. Ikenberry (2014) points out that, as the overwhelmingly global power once concentrated within the United States dispersed with the arrival of new power challengers in different parts of the world, new struggles over global rules and institutions are emerging. At the very least, as emphasised by Mearsheimer (2013), great powers do not trust one another, as they worry about other countries’ capabilities and intentions.
Not without reason, Mearsheimer (2013) argues that the United States did not and does not tolerate peer competitors, adding that the United States has demonstrated this clearly during the twentieth century.
For these reasons, we cannot expect that a hegemon will stay inactive when watching the rise of potential challengers. An established great power, holding an almost global hegemonic position as the United States does, has the capacity to respond to the challenges arising from power contenders, and there are clear indications, past and present, that it will act to preserve its dominant power position, even within an international system that has become more multilateral in comparison with the Cold War period. Not without reason, Mearsheimer (2013) argues that the United States did not and does not tolerate peer competitors, adding that the United States has demonstrated this clearly during the twentieth century. One just has to remember that in the late 1980s, when Japan was close to economically overtaking the United States. at the global level, various United States administrations actively worked against it, refusing Japan more decision-making rights within international organisations like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund, even though Japan had become a major donor to both organisations. Obviously, the previous Japanese challenge to the United States’ dominance was only economic. Neither will the United States allow other challengers to succeed in undermining its dominant position, even in distant regional settings. Mearsheimer (2001) reminds us that the dominant power will act at the regional level to ensure that no challenge to its own global position will take place, since the crucial task is to block potential peer competitors, even within distant regional settings.
When evaluating the influence of a hegemon it is worth remembering that this goes beyond a focus on military capabilities, even though such capabilities are essential, and include the hegemon’s ability to disguise its ambitions and interests by pretending that it provides global public goods, which in reality satisfy primarily its own interests. More importantly, as pointed out by Griffiths, O’Callaghan and Roach (2002), all hegemonic states enjoy ‘structural power’, which permits the hegemon to occupy a central position within its own system, as well as shape other states’ preferences. As emphasised by Kupchan (2014), a hegemon also strives to generate a normative and ideological dominance, in support of its power dominance. Indeed, Gilpin, in his seminal influential work on war and change, emphasises that a major power aims to create social structures to serve its hegemonic interests, consequently supporting its domineering position with rules, institutions, and organisational principles, supporting, indeed screening and protecting, its power position with normative dominance (Gilpin 1981).
one can also reasonably assume that when a hegemonic country introduces a new geopolitical or regional concept of space, such as the Indo-Pacific framework, will be of foremost importance to its own strategy of dominance. Indeed, the Indo-Pacific framework signals the re-mapping of geopolitical space, with little, if any, historical relevance.
By considering these arguments describing the behaviour of a typical hegemonic power, it is rather consistent to assume that a country, such as the United States, which holds a nearly global like hegemonic position, will use its position and capabilities to support its own power position in different regional settings so as to ward off any potential competitor. For this reason, one can also reasonably assume that when a hegemonic country introduces a new geopolitical or regional concept of space, such as the Indo-Pacific framework, will be of foremost importance to its own strategy of dominance. Indeed, the Indo-Pacific framework signals the re-mapping of geopolitical space, with little, if any, historical relevance. From a historical perspective, the Indian and Pacific Oceans have been perceived as separate maritime spaces. What marries them into one geopolitical space is an invented geopolitical strategy facilitating the strategic power interests of the existing hegemon. What is more, a hegemon or hegemon-like state will not introduce or favour a new geopolitical concept if it goes against its own strategic interests.
Indeed, from a United States perspective, the Indo-Pacific strategy not only re-strengthens, at least from a hegemonic perspective, its role within the older geopolitical concept of Asia-Pacific, but now extends this influence, from a conceptual perspective, to include the Indian Ocean, as well. One can further argue that the adoption of the Indo-Pacific approach by the United States comes at a time when we can observe considerable changes in the power configuration within East Asia (which encompasses Northeast and Southeast Asia) and to a lesser extent within South Asia. Certain changes in the regional power configuration, namely the rise of China – not only as an economic but increasingly as a military and especially as a maritime power – generate considerable challenges from the perspective of hegemonic power competition. While the strategic challenge that China, as a rising power, generates to the United States quasi hegemonic position is so far limited to a regional challenge, instead of a global challenge, still, based on hegemony theory, the existing hegemon cannot allow such a challenge to take place.
The late embracing of the Indo-Pacific concept by the United States further supports the position that it is being employed as a strategic instrument to counter a rising power and a potential challenger to its global quasi-hegemonic power position. We may remember that the origin of the Indo-Pacific concept is associated with the previous Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and his ‘Free and Open Indo-Pacific’ concept. Shinzo Abe mentioned it as early as 2007 when addressing the Indian parliament and began frequently restating it from 2016 onwards. This was part of his intention that Japan should take a more active role in East Asia and beyond. As such, the Indo-Pacific concept was born out of the political-strategic considerations of a regional actor within East Asia. Only later, around 2018, did the United States become considerably interested in the concept, at a time when the potential challenges from rising countries increased – not only from China; one may also consider India’s rise in this context. In 2018, the United States administration even changed the name of its Pacific Command to United States Indo-Pacific Command to highlight its changing geopolitical perspective and to address the increasing regional challenges it faced from a rising China. Not without reason was the replacement of the previous Asia-Pacific concept with the Indo-Pacific concept aimed at integrating India, another rising power in Asia, more firmly with the hegemonic interests of the United States. In academic terms, one could argue that this may represent a strategy of accommodation, in which an existing hegemon accommodates a rising power by offering political and strategic space for that country. It is a strategy the United States followed previously with China until China started to become a too fundamental strategic challenge to the United States hierarchic position. One may wonder if this may also happen to India, once India becomes too powerful to be contained within a United States hegemonic project. However, for the time being, India seems to feel quite comfortable within the geopolitical space it has been offered by the existing quasi-global hegemon. As revealed by Paul T.V (2016) the strategy of accommodation is not only quite a challenging undertaking – as the hegemon has to offer political status, leadership responsibilities, and even a sphere of influence to a rising country – but in the long run the implications are that this will weaken, if not undermine, the hegemon’s own position, thus indicating the limitation of such a strategy. After all, a hegemon is rather unwilling to give up its dominant position voluntarily, though a strategy of accommodation may buy some time and allow it to employ a strategy of divide-and-rule by offering support to a potential weaker power contender when addressing the challenges of a more powerful contender. There can be no less doubt that the ongoing border conflicts between India and China and the emerging regional power competition between them facilitate India’s readiness to become increasingly enveloped in a stronger relationship with the United States which, by the way, contradicts India’s previous entrenched national strategy of non-alignment in global power politics. Consequently, drafting India into its power orbit enhances the United States’ strategic influence in regions where it is not even a resident power, like East, Southeast, or South Asia.
There can be no less doubt that the ongoing border conflicts between India and China and the emerging regional power competition between them facilitate India’s readiness to become increasingly enveloped in a stronger relationship with the United States which, by the way, contradicts India’s previous entrenched national strategy of non-alignment in global power politics.
Therefore, a hegemonic state will try to manipulate even distant regional settings in its favour, to arrest the rise of potential challengers to its dominant position, even by facilitating the introduction of a new geopolitical concept, like the Indo-Pacific, which ignores local perceptions of regional cooperation dynamics, the Bay of Bengal approach or ASEAN. While there are some claims that the Indo-Pacific approach does not represent a challenge to ASEAN, a position that is widely disputed, the more specific issue is that the Indo-Pacific approach does not contribute or offer support to those local-based regional cooperation processes from a conceptual perspective. Therefore, while one has to recognise that more recent regional cooperation processes within the Bay of Bengal are less dynamic for the time being, it does not mean that such a regional cooperation process is altogether missing. As stated by Amrith (2013), Asian economic connections led to renewed interest in the Bay of Bengal as a focus for regional cooperation. Indeed, BIMSTEC[1] which was established in 1997, does provide focus on regional cooperation.
BIMSTEC creates political space for economic cooperation by addressing common challenges like underdevelopment. Consequently, offering a strategic vision for national development to its member countries, a focus fundamentally different from the geopolitical outlook of the Indo-Pacific regional hegemonic project, with its focus on military and especially maritime power distribution. Another crucial difference is that, while the Indo-Pacific strategy is a rather recent invention, regional recognition of the Bay of Bengal as a particular and unique geographic location for regional cooperation, particularly as a centre for trade and cultural migration, goes back centuries, if not millennia. As such, the Bay of Bengal commands a rich history as a historically recognised cultural and trade-inspired region. Yet, with geopolitical concepts based on hegemonic interests, such home-grown sources of regional cooperation are not recognised or supported only if they would fit the interests of the hegemon. It is evident that the Indo-Pacific concept, from a conceptual perspective, also ignores the ASEAN regional cooperation process. As such, the Indo-Pacific approach represents an artificial strategic overlay, not linked with local beads regional cooperation dynamics, even when a regional cooperation process is very well established, as is the case with ASEAN. With regard to the Indo-Pacific concept, ASEAN’s statement on the Indo-Pacific (ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific 2019) clearly indicates that the perception of the Indo-Pacific area is a contiguous geographic space is misleading and not appropriate, even though the two geopolitical spaces are geographically connected. Indeed, while the Bay of Bengal and the ASEAN regional cooperation favour regional cooperation characterised by horizontal relationships, facilitating the cooperation of countries within the region to address common challenges, the Indo-Pacific approach represent a vertical power arrangement, where a dominant power is projecting its influence onto the regional level.
However, it should not come as too much of a surprise that a hegemon’s regional strategy, which primarily focuses on supporting its own power interests, has little to say about regional cooperation processes initiated by the people living in that region. Indeed, a global acting hegemon has only a limited interest in the empowerment of independent regional cooperation projects, since they could signal the creation of a more independent political sphere. As Mearsheimer (2013) asserts, based on its superior standing and its need to defend this position, a hegemon has always an inclination to interfere in and re-order the political outlook of even distant regions. We may take into consideration what Mearsheimer (2013) made earlier, that the United States will ensure that it will dominate the commanding heights in Asia. For all these reasons, the Indo-Pacific approach should be recognised as the newest geopolitical strategy supporting the United States’ hegemonic position in Asia.
Bibliography
Mearsheimer, John J (2001) The Tragedy of Great Power Politics (2001), W.W Norton & Company: New York
Mearsheimer, John J (2013) Structural Realism. In: Dunne T, Kurki M., Smith S (eds) International Relations Theories Discipline and Diversity, 3rd ed., Oxford University Press: Oxford. pp. 77-93
Ikenberry, G. J. (2014) Introduction: power, order, and change in world politics. In: Ikenberry, G. J. (ed.) Power, order, and change in world politics. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, pp.1-16.
Griffiths, M, O’Callaghan T, Roach S T (2002) International Relations: The Key Concepts 2nd; Martin Griffiths, Routledge
Kupchan, C. A. (2014) Unpacking hegemony: the social foundations of hierarchical order. In: Ikenberry, G. J. (ed.) Power, order, and change in world politics. Cambridge, University Press Cambridge, pp. 19-60.
Gilpin, R. (2010) War and Change in World Politics, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge.
Paul T.V. (2016) The accommodation of rising powers in world politics. In: Paul, T. V. (ed.) Accommodating rising powers past, present, and future. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, pp. 3 32.
Amrith, S. S. (2013) Crossing the Bay of Bengal: The furies of nature and the fortunes of migrants By Sunil S. Amrith Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific 2019, available at: https://asean.org/asean-outlook-on-the-indo-pacific/
Notes
[1] BIMSTEC has seven members: Thailand, Myanmar, Bangladesh, India, Bhutan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka.
Feature Image credit: War on the Rocks






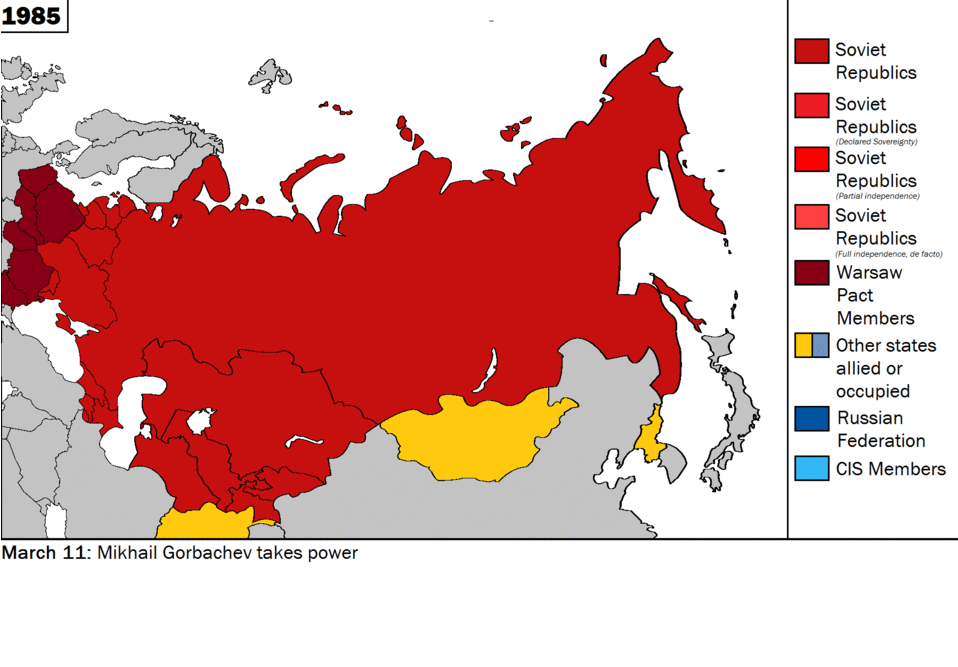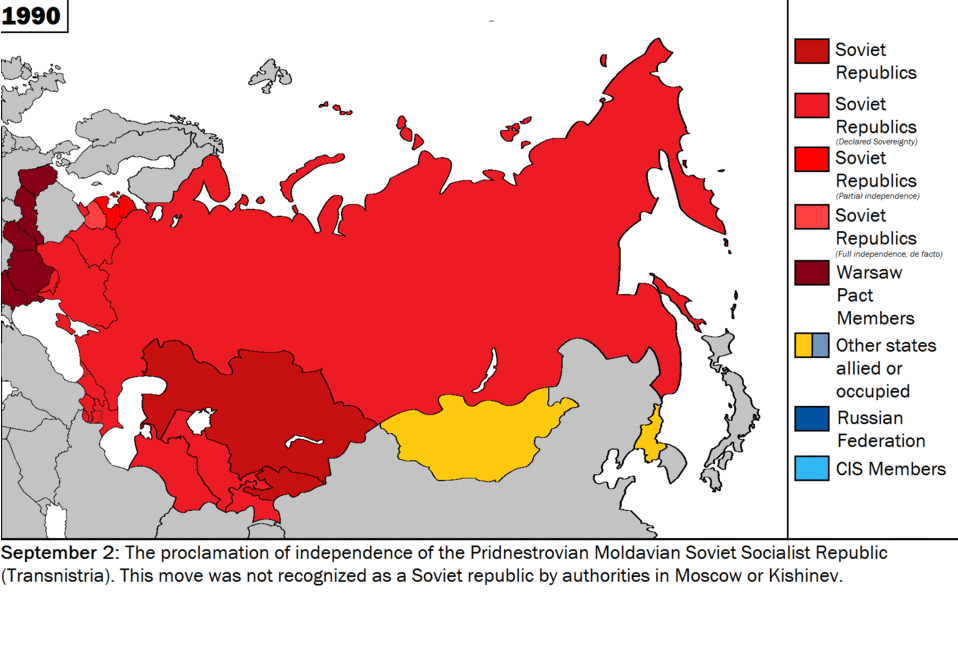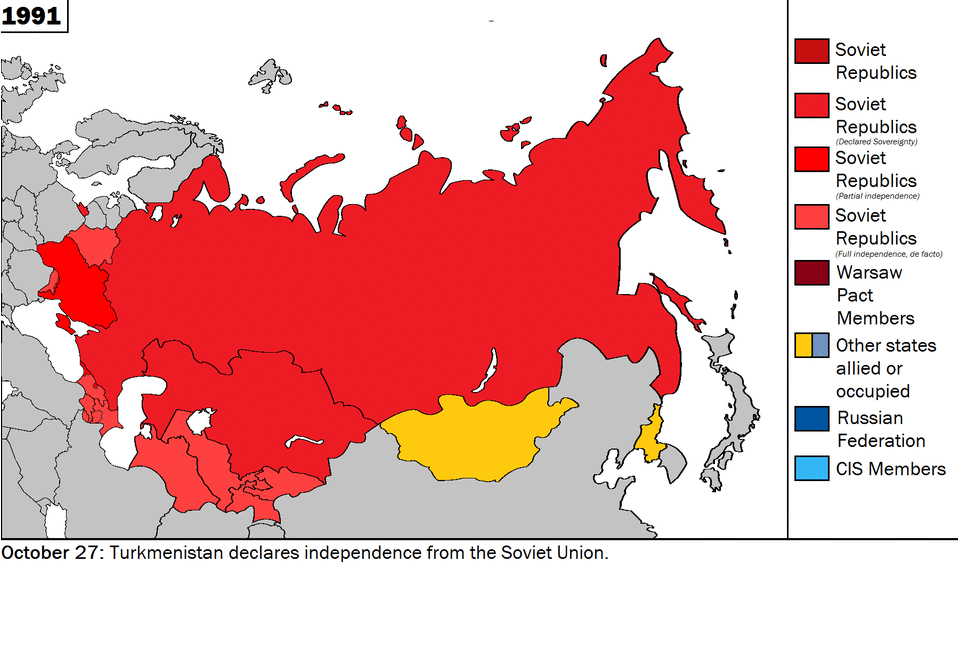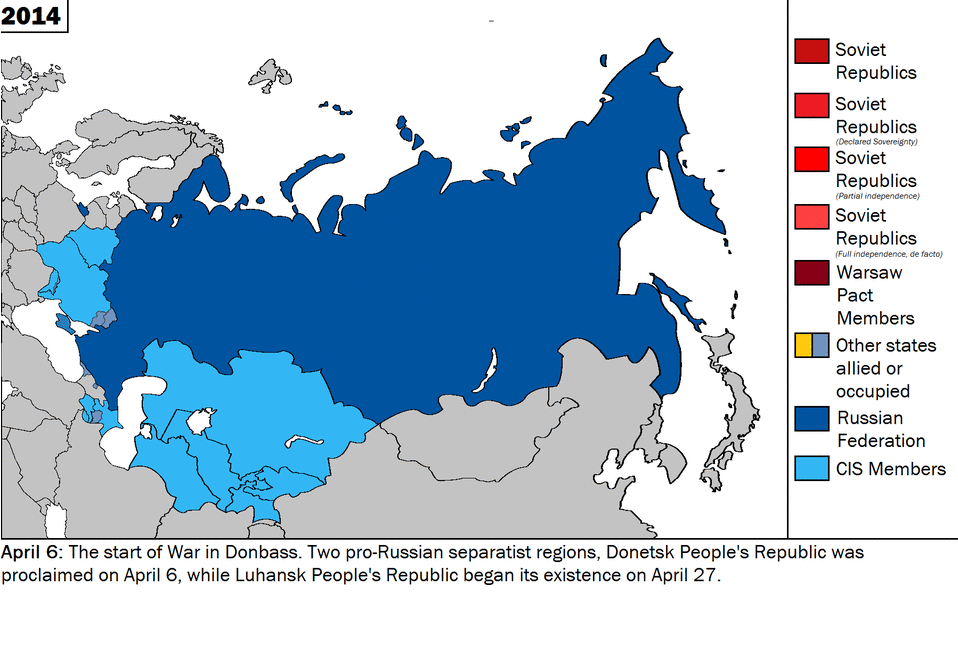





















 CNN and other U.S. media blamed Russia for destroying the movie theater in Mariupol when eyewitness said it was Azov militants within the Ukrainian army. Source:
CNN and other U.S. media blamed Russia for destroying the movie theater in Mariupol when eyewitness said it was Azov militants within the Ukrainian army. Source: