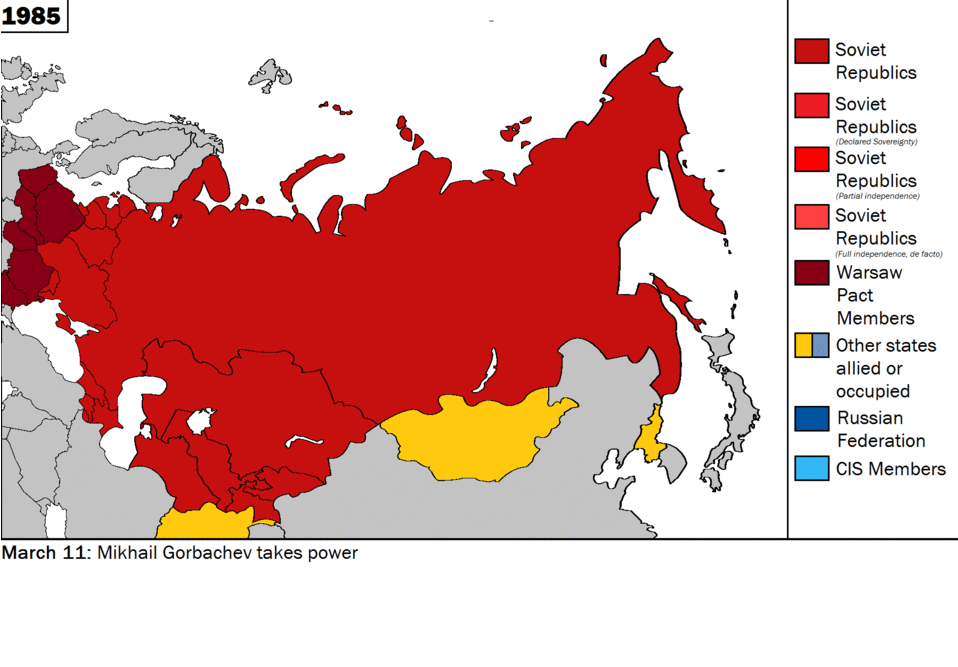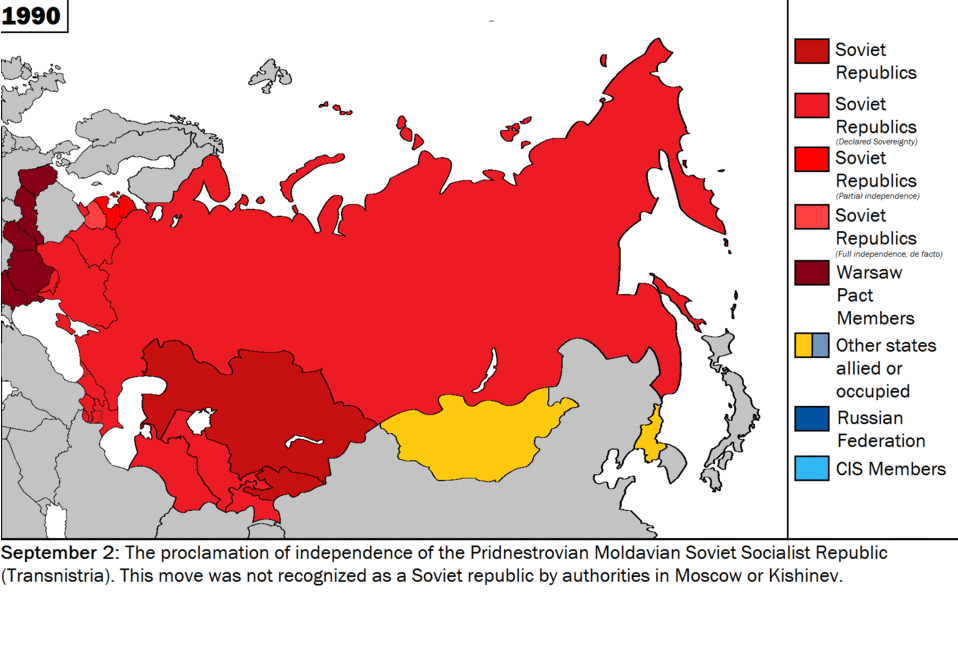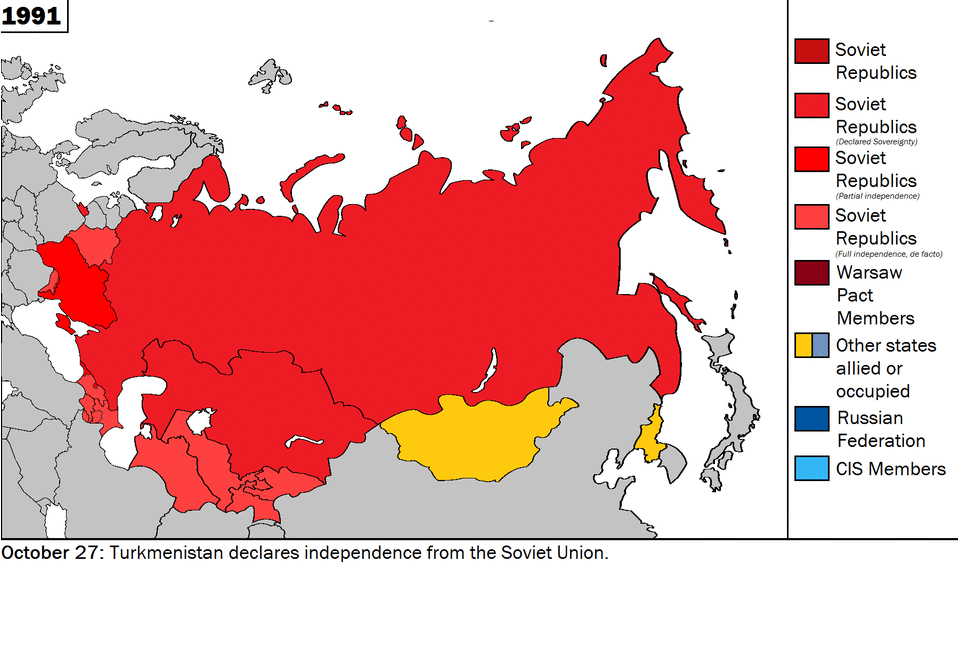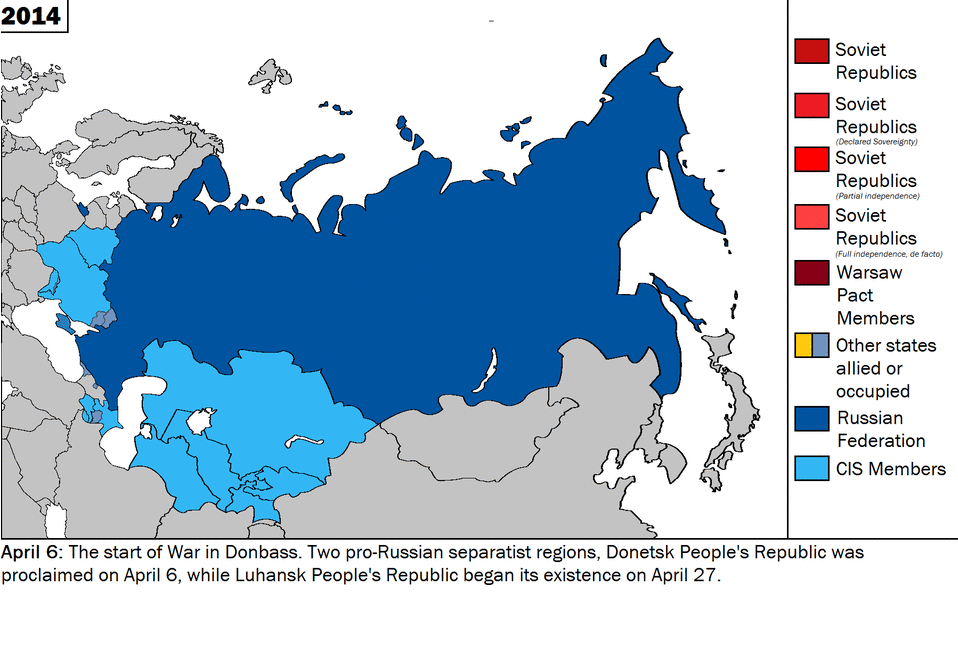
In a world shaped by the iron logic of markets and national interests, Vladimir Putin’s atavistic war of conquest has mystified the “deep” strategists of realpolitik. Their mistake was to forget that under global capitalism, cultural, ethnic, and religious conflicts are the only forms of political struggle left.
With the Russian invasion of Ukraine, we are entering a new phase of warfare and global politics. Aside from a heightened risk of nuclear catastrophe, we are already in a perfect storm of mutually reinforcing global crises – the pandemic, climate change, biodiversity loss, and food and water shortages. The situation exhibits a basic madness: at a time when humanity’s very survival is jeopardized by ecological (and other) factors, and when addressing those threats should be prioritized over everything else, our primary concern has suddenly shifted – again – to a new political crisis. Just when global cooperation is needed more than ever, the “clash of civilizations” returns with a vengeance.
Why does this happen? As is often the case, a little Hegel can go a long way toward answering such questions. In the Phenomenology of Spirit, Hegel famously describes the dialectic of master and servant, two “self-consciousnesses” locked in a life-or-death struggle. If each is ready to risk his own life to win, and if both persist in this, there is no winner: one dies, and the survivor no longer has anyone to recognize his own existence. The implication is that all of history and culture rest on a foundational compromise: in the eye-to-eye confrontation, one side (the future servant) “averts its eyes,” unwilling to go to the end.
But Hegel would hasten to note that there can be no final or lasting compromise between states. Relationships between sovereign nation-states are permanently under the shadow of potential war, with each epoch of peace being nothing more than a temporary armistice. Each state disciplines and educates its own members and guarantees civic peace among them, and this process produces an ethic that ultimately demands acts of heroism – a readiness to sacrifice one’s life for one’s country. The wild, barbarian relations between states thus serve as the foundation of the ethical life within states.
North Korea represents the clearest example of this logic, but there are also signs that China is moving in the same direction. According to friends in China (who must remain unnamed), many authors in Chinese military journals now complain that the Chinese army hasn’t had a real war to test its fighting ability. While the United States is permanently testing its army in places like Iraq, China hasn’t done so since its failed intervention in Vietnam in 1979.
At the same time, Chinese official media have begun to hint more openly that since the prospect of Taiwan’s peaceful integration into China is dwindling, a military “liberation” of the island will be needed. As ideological preparation for this, the Chinese propaganda machine has increasingly urged nationalist patriotism and suspicion toward everything foreign, with frequent accusations that the US is eager to go to war for Taiwan. Last fall, Chinese authorities advised the public to stock up on enough supplies to survive for two months “just in case.” It was a strange warning that many perceived as an announcement of imminent war.
This tendency runs directly against the urgent need to civilize our civilizations and establish a new mode of relating to our environs. We need universal solidarity and cooperation among all human communities, but this objective is made far more difficult by the rise of sectarian religious and ethnic “heroic” violence and a readiness to sacrifice oneself (and the world) for one’s specific cause. In 2017, the French philosopher Alain Badiou noted that the contours of a future war are already discernible. He foresaw:
“…the United States and their Western-Japanese group on the one side, China and Russia on the other side, atomic arms everywhere. We cannot but recall Lenin’s statement: ‘Either revolution will prevent the war or the war will trigger revolution.’ This is how we can define the maximal ambition of the political work to come: for the first time in history, the first hypothesis – revolution will prevent the war – should realize itself, and not the second one – a war will trigger revolution. It is effectively the second hypothesis which materialized itself in Russia in the context of the First World War, and in China in the context of the second. But at what price! And with what long-term consequences!”
The Limits of Realpolitik
Civilizing our civilizations will require radical social change – a revolution, in fact. But we cannot afford to hope that a new war will trigger it. The far more likely outcome is the end of civilization as we know it, with the survivors (if there are any) organized in small authoritarian groups. We should harbor no illusions: in some basic sense, World War III has already begun, though for now it is still being fought mostly through proxies.
Abstract calls for peace are not enough. “Peace” is not a term that allows us to draw the key political distinction that we need. Occupiers always sincerely want peace in the territory they hold. Nazi Germany wanted peace in occupied France, Israel wants peace in the occupied West Bank, and Russian President Vladimir Putin wants peace in Ukraine. That is why, as the philosopher Étienne Balibar once put it, “pacifism is not an option.” The only way to prevent another Great War is by avoiding the kind of “peace” that requires constant local wars for its maintenance.
Whom can we rely on under these conditions? Should we place our confidence in artists and thinkers, or in pragmatic practitioners of realpolitik? The problem with artists and thinkers is that they, too, can lay the foundation for war. Recall William Butler Yeats’s apt verse: “I have spread my dreams under your feet, / Tread softly because you tread on my dreams.” We should apply these lines to poets themselves. When they spread their dreams under our feet, they should spread them carefully because actual people will read them and act upon them. Recall that the same Yeats continuously flirted with Fascism, going so far as to voice his approval of Germany’s anti-Semitic Nuremberg Laws in August 1938.
Plato’s reputation suffers because of his claim that poets should be thrown out of the city. Yet this is rather sensible advice, judging from the experience of recent decades, when the pretext for ethnic cleansing has been prepared by poets and “thinkers” like Putin’s house ideologue, Aleksandr Dugin. There is no longer ethnic cleansing without poetry, because we live in an era that is supposedly post-ideological. Since great secular causes no longer have the force to mobilize people for mass violence, a larger sacred motive is needed. Religion or ethnic belonging serve this role perfectly (pathological atheists who commit mass murder for pleasure are rare exceptions).
Realpolitik is no better guide. It has become a mere alibi for ideology, which often evokes some hidden dimension behind the veil of appearances in order to obscure the crime that is being committed openly. This double mystification is often announced by describing a situation as “complex.” An obvious fact – say, an instance of brutal military aggression – is relativized by evoking a “much more complex background.” The act of aggression is really an act of defense.
This is exactly what is happening today. Russia obviously attacked Ukraine, and is obviously targeting civilians and displacing millions. And yet commentators and pundits are eagerly searching for “complexity” behind it.
There is complexity, of course. But that does not change the basic fact that Russia did it. Our mistake was that we did not interpret Putin’s threats literally enough; we thought he was just playing a game of strategic manipulation and brinkmanship. One is reminded of the famous joke that Sigmund Freud quotes:
“Two Jews met in a railway carriage at a station in Galicia. ‘Where are you going?’ asked one. ‘To Cracow,’ was the answer. ‘What a liar you are!’ broke out the other. ‘If you say you’re going to Cracow, you want me to believe you’re going to Lemberg. But I know that in fact you’re going to Cracow. So why are you lying to me?’”
When Putin announced a military intervention, we didn’t take him literally when he said he wanted to pacify and “denazify” Ukraine. Instead, the reproach from disappointed “deep” strategists amounts to: “Why did you tell me you are going to occupy Lviv when you really want to occupy Lviv?”
This double mystification exposes the end of realpolitik. As a rule, realpolitik is opposed to the naivety of binding diplomacy and foreign policy to (one’s version of) moral or political principles. Yet in the current situation, it is realpolitik that is naive. It is naive to suppose that the other side, the enemy, is also aiming at a limited pragmatic deal.
Force and Freedom
During the Cold War, the rules of superpower behavior were clearly delineated by the doctrine of mutual assured destruction (MAD). Each superpower could be sure that if it decided to launch a nuclear attack, the other side would respond with full destructive force. As a result, neither side started a war with the other.
By contrast, when North Korea’s Kim Jong-un talks about dealing a devastating blow to the US, one cannot but wonder where he sees his own position. He talks as if he is unaware that his country, himself included, would be destroyed. It is as if he is playing an altogether different game called NUTS (Nuclear Utilization Target Selection), whereby the enemy’s nuclear capabilities can be surgically destroyed before it can counterstrike.
Over the past few decades, even the US has oscillated between MAD and NUTS. Though it acts as if it continues to trust the MAD logic in its relations with Russia and China, it has occasionally been tempted to pursue a NUTS strategy vis-à-vis Iran and North Korea. With his hints about possibly launching a tactical nuclear strike, Putin follows the same reasoning. The very fact that two directly contradictory strategies are mobilized simultaneously by the same superpower attests to the fantasy character of it all.
Unfortunately for the rest of us, MADness is passé. Superpowers are increasingly testing each other, experimenting with the use of proxies as they try to impose their own version of global rules. On March 5, Putin called the sanctions imposed on Russia the “equivalent of a declaration of war.” But he has repeatedly stated since then that economic exchange with the West should continue, emphasizing that Russia is keeping its financial commitments and continuing to deliver hydrocarbons to Western Europe.
In other words, Putin is trying to impose a new model of international relations. Rather than cold war, there should be hot peace: a state of permanent hybrid war in which military interventions are declared under the guise of peacekeeping and humanitarian missions.
Hence, on February 15, the Russian Duma (parliament) issued a declaration expressing “its unequivocal and consolidated support for the adequate humanitarian measures aimed at providing support to residents of certain areas of the Donetsk and Lugansk regions of Ukraine who have expressed a desire to speak and write in Russian language, who want freedom of religion to be respected, and who do not support the actions of the Ukrainian authorities violating their rights and freedoms.”
How often in the past have we heard similar arguments for US-led interventions in Latin America or the Middle East and North Africa? While Russia shells cities and bombs maternity wards in Ukraine, international commerce should continue. Outside of Ukraine, normal life should go on. That is what it means to have a permanent global peace sustained by never-ending peacekeeping interventions in isolated parts of the world.
Can anyone be free in such a predicament? Following Hegel, we should make a distinction between abstract and concrete freedom, which correspond to our notions of freedom and liberty. Abstract freedom is the ability to do what one wants independently of social rules and customs; concrete freedom is the freedom that is conferred and sustained by rules and customs. I can walk freely along a busy street only when I can be reasonably sure that others on the street will behave in a civilized way toward me – that drivers will obey traffic rules, and that other pedestrians will not rob me.
But there are moments of crisis when abstract freedom must intervene. In December 1944, Jean-Paul Sartre wrote: “Never were we freer than under the German occupation. We had lost all our rights, and first of all our right to speak. They insulted us to our faces. … And that is why the Resistance was a true democracy; for the soldier, as for his superior, the same danger, the same loneliness, the same responsibility, the same absolute freedom within the discipline.”
Sartre was describing freedom, not liberty. Liberty is what was established when post-war normality returned. In Ukraine today, those who are battling the Russian invasion are free and they are fighting for liberty. But this raises the question of how long the distinction can last. What happens if millions more people decide that they must freely violate the rules in order to protect their liberty? Is this not what drove a Trumpian mob to invade the US Capitol on January 6, 2021?
The Not-so-Great Game
We still lack a proper word for today’s world. For her part, the philosopher Catherine Malabou believes we are witnessing the beginning of capitalism’s “anarchist turn”: “How else are we to describe such phenomena as decentralized currencies, the end of the state’s monopoly, the obsolescence of the mediating role played by banks, and the decentralization of exchanges and transactions?”
Those phenomena may sound appealing, but with the gradual disappearance of the state’s monopoly, state-imposed limits to ruthless exploitation and domination will also disappear. While anarcho-capitalism aims at transparency, it also “simultaneously authorizes the large-scale but opaque use of data, the dark web, and the fabrication of information.”
To prevent this descent into chaos, Malabou observes, policies increasingly follow a path of “Fascist evolution…with the excessive security and military build-up that goes along with it. Such phenomena do not contradict a drive towards anarchism. Rather, they indicate precisely the disappearance of the state, which, once its social function has been removed, expresses the obsolescence of its force through the use of violence. Ultra-nationalism thus signals the death agony of national authority.”
Viewed in these terms, the situation in Ukraine is not one nation-state attacking another nation-state. Rather, Ukraine is being attacked as an entity whose very ethnic identity is denied by the aggressor. The invasion is justified in the terms of geopolitical spheres of influence (which often extend well beyond ethnic spheres, as in the case of Syria). Russia refuses to use the word “war” for its “special military operation” not just to downplay the brutality of its intervention but above all to make clear that war in the old sense of an armed conflict between nation-states does not apply.
The Kremlin wants us to believe that it is merely securing “peace” in what it considers its geopolitical sphere of influence. Indeed, it is also already intervening through its proxies in Bosnia and Kosovo. On March 17, the Russian ambassador to Bosnia, Igor Kalabukhov, explained that, “If [Bosnia] decides to be a member of any alliance [such as NATO], that is an internal matter. Our response is a different matter. Ukraine’s example shows what we expect. Should there be any threat, we will respond.”
Moreover, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov has gone so far as to suggest that the only comprehensive solution would be to demilitarize all of Europe, with Russia with its army maintaining peace through occasional humanitarian interventions. Similar ideas abound in the Russian press. As the political commentator Dmitry Evstafiev explains in a recent interview with a Croatian publication: “A new Russia is born which lets you know clearly that it doesn’t perceive you, Europe, as a partner. Russia has three partners: USA, China, and India. You are for us a trophy which shall be divided between us and Americans. You didn’t yet get this, although we are coming close to this.”
Dugin, Putin’s court philosopher, grounds the Kremlin’s stance in a weird version of historicist relativism. In 2016, he said:
“Post-modernity shows that every so-called truth is a matter of believing. So we believe in what we do, we believe in what we say. And that is the only way to define the truth. So we have our special Russian truth that you need to accept…. If the United States does not want to start a war, you should recognize that United States is not any more a unique master. And [with] the situation in Syria and Ukraine, Russia says, ‘No you are not any more the boss.’ That is the question of who rules the world. Only war could decide really.”
This raises an obvious question: What about the people of Syria and Ukraine? Can they not also choose their truth and belief, or are they just a playground – or battlefield – of the big “bosses”? The Kremlin would say they don’t count in the big division of power. Within the four spheres of influence, there are only peacekeeping interventions. War proper happens only when the four big bosses cannot agree on the borders of their spheres – as in the case of China’s claims to Taiwan and the South China Sea.
A New Non-Alignment
But if we can be mobilized only by the threat of war, not by the threat to our environment, the liberty we will get if our side wins may not be worth having. We are faced with an impossible choice: if we make compromises to maintain peace, we are feeding Russian expansionism, which only a “demilitarization” of all of Europe will satisfy. But if we endorse full confrontation, we run the high risk of precipitating a new world war. The only real solution is to change the lens through which we perceive the situation.
While the global liberal-capitalist order is obviously approaching a crisis at many levels, the war in Ukraine is being falsely and dangerously simplified. Global problems like climate change play no role in the hackneyed narrative of a clash between barbaric-totalitarian countries and the civilized, free West. And yet the new wars and great-power conflicts are also reactions to such problems. If the issue is survival on a planet in trouble, one should secure a stronger position than others. Far from being the moment of clarifying truth, and when the basic antagonism is laid bare, the current crisis is a moment of deep deception.
While we should stand firmly behind Ukraine, we must avoid the fascination with war that has clearly seized the imaginations of those who are pushing for an open confrontation with Russia. Something like a new non-aligned movement is needed, not in the sense that countries should be neutral in the ongoing war, but in the sense that we should question the entire notion of the “clash of civilizations.”
According to Samuel Huntington, who coined the term, the stage for a clash of civilizations was set at the Cold War’s end, when the “iron curtain of ideology” was replaced by the “velvet curtain of culture.” At first blush, this dark vision may appear to be the very opposite of the end-of-history thesis advanced by Francis Fukuyama in response to the collapse of communism in Europe. What could be more different from Fukuyama’s pseudo-Hegelian idea that the best possible social order humanity could devise had at last been revealed to be capitalist liberal democracy?
We can now see that the two visions are fully compatible: the “clash of civilizations” is the politics that comes at the “end of history.” Ethnic and religious conflicts are the form of struggle that fits with global capitalism. In an age of “post-politics” – when politics proper is gradually replaced by expert social administration – the only remaining legitimate sources of conflict are cultural (ethnic, religious). The rise of “irrational” violence follows from the depoliticization of our societies.
Within this limited horizon, it is true that the only alternative to war is a peaceful coexistence of civilizations (of different “truths,” as Dugin put it, or, to use a more popular term today, of different “ways of life”). The implication is that forced marriages, homophobia, or the rape of women who dare to go out in public alone are tolerable if they happen in another country, so long as that country is fully integrated into the global market.
The new non-alignment must broaden the horizon by recognizing that our struggle should be global – and by counseling against Russophobia at all costs. We should offer our support to those within Russia who are protesting the invasion. They are not some abstract coterie of internationalists; they are the true Russian patriots – the people who truly love their country and have become deeply ashamed of it since February 24. There is no more morally repulsive and politically dangerous saying than, “My country, right or wrong.” Unfortunately, the first casualty of the Ukraine war has been universality.
This essay was published earlier in Project Syndicate.