
Download
[/powerkit_button]



The 15th BRICS Summit will be held next week from the 22nd to the 24th of August in Johannesburg under the chairmanship of South Africa. Unlike in the past when the West largely ignored the summits as of little consequence, the 15th Summit has got the world’s attention in a major way. Given the current turmoil in the world order and the realisation in much of the world that the West is largely responsible for the unending wars and interventions, this summit has assumed enormous importance. To put it bluntly, the BRICS is being seen as having the potential to end Western dominance and reshape the world into a more equitable and multipolar world order. The summit, which South Africa hosts next week, could mark a significant step in the reconfiguration of geopolitical power in the not-too-distant future.
Already, BRICS countries represent over 40% of the global population and an estimated 30% of its GDP, and with China expected to overtake the United States as early as 2035 as the world’s largest economy, many sovereign states are eager to establish themselves for a de-dollarised future. 40 countries have expressed their interest to join BRICS, while 23 countries have formally applied, including Argentina, Iran, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Indonesia, Thailand, Cuba, Egypt, and Nigeria. A total of 67 countries, including 53 African states have been invited to the BRICS Summit 2023. This is a significant development. The important issues likely to be discussed at the summit include the expansion of BRICS and the possible introduction of BRICS currency. As a prelude, the joint statement of BRICS’ foreign ministers meeting in June 2023 shows the expanding domains of cooperation that included international security and world order. The joint statement is reproduced below.
– Team TPF

Joint Statement of the BRICS Ministers of Foreign Affairs and International Relations Cape Town, South Africa 1 June 2023
1. The BRICS Ministers of Foreign Affairs and International Relations met on 1 June 2023 in Cape Town, South Africa. They exchanged views on major global and regional trends and issues. They reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening the framework of BRICS cooperation under the three pillars of political and security, economic and financial, and cultural and people-to-people cooperation upholding the BRICS spirit featuring mutual respect and understanding, equality, solidarity, openness, inclusiveness, and consensus.
2. The Ministers reiterated their commitment to strengthening multilateralism and upholding international law, including the purposes and principles enshrined in the Charter of the United Nations (UN) as its indispensable cornerstone, and the central role of the UN in an international system in which sovereign states cooperate to maintain peace and security, advance sustainable development, ensure the promotion and protection of democracy, human rights and fundamental freedoms for all, and promoting cooperation based on the spirit of solidarity, mutual respect, justice and equality.
3. The Ministers expressed concern about the use of unilateral coercive measures, which are incompatible with the principles of the Charter of the UN and produce negative effects notably in the developing world. They reiterated their commitment to enhancing and improving global governance by promoting a more agile, effective, efficient, representative and accountable international and multilateral system.
4. The Ministers recalled UN General Assembly (UNGA) Resolution 75/1 and reiterated the call for reforms of the principal organs of the United Nations. They recommitted to instil new life in the discussions on the reform of the UN Security Council (UNSC) and continue the work to revitalise the General Assembly and strengthen the Economic and Social Council. They recalled the 2005 World Summit Outcome document and reaffirmed the need for a comprehensive reform of the UN, including its Security Council, with a view to making it more representative, effective and efficient, and to increase the representation of the developing countries so that it can adequately respond to global challenges. China and Russia reiterated the importance they attach to the status and role of Brazil, India and South Africa in international affairs and supported their aspiration to play a greater role in the UN.
5. The Ministers reaffirmed the importance of the G20 to continue playing the role of the premier multilateral forum in the field of economic cooperation that comprises both developed and developing countries where major economies jointly seek solutions to global challenges. They looked forward to the successful hosting of the 18th G20 Summit under the Indian G20 Presidency. They noted the opportunities to build sustained momentum for change by India, Brazil and South Africa chairing the G20 from 2023 to 2025 and expressed support for continuity and collaboration in their G20 presidencies and wish them all success in their endeavours.
6. The Ministers called for the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in its three dimensions – economic, social and environmental – in a balanced and integrated manner by mobilising the means required to implement the 2030 Agenda. They highlighted in this regard that the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Summit, to be held in New York in September 2023, constitutes a unique opportunity for renewing international commitment to the implementation of the 2030 Agenda.
7. The Ministers recognised the impact on the world economy from unilateral approaches in breach of international law and they also noted that the situation is complicated further by unilateral economic coercive measures, such as sanctions, boycotts, embargoes and blockades.
8. The Ministers expressed their support for the free, open, transparent, fair, predictable, inclusive, equitable, non-discriminatory and rules-based multilateral trading system with the World Trade Organisation (WTO) at its core, with special and differential treatment (S&DT) for developing countries, including Least Developed Countries. They stressed their support to work towards positive and meaningful outcomes on the issues at the 13th Ministerial Conference (MC13). They committed to engage constructively to pursue the necessary WTO reform with a view to presenting concrete deliverables to MC13. They called for the restoration of a fully and well-functioning dispute settlement system accessible to all members by 2024, and the selection of new Appellate Body Members without further delay. They condemned unilateral protectionist measures under the pretext of environmental concerns such as unilateral and discriminatory carbon border adjustment mechanisms, taxes and other measures.
9. They supported a robust Global Financial Safety Net with a quota-based and adequately resourced International Monetary Fund (IMF) at its centre. They called on continuing the process of IMF governance reform under the 16th General Review of Quotas, including a new quota formula as a guide, to be completed by 15 December 2023.
10. The Ministers congratulated Ms Dilma Rousseff, former President of the Federative Republic of Brazil, as President of the New Development Bank (NDB) and expressed confidence that it will contribute to strengthening the NDB in effectively achieving its mandate. They encouraged the NDB to follow the member-led and demand-driven principle, mobilise financing from diversified sources, enhance innovation and knowledge exchange, assist member countries in achieving the SDGs and further improve efficiency and effectiveness to fulfil its mandate, aiming to be a premier multilateral development institution.
11. The Ministers emphasised the importance of financial inclusion so that citizens can reap the benefits of economic growth and prosperity and welcomed the many new technological instruments for financial inclusion, developed in BRICS countries, that can contribute to ensuring the citizens full participation in the formal economy.
12. Ministers underscored the importance of encouraging the use of local currencies in international trade and financial transactions between BRICS as well as their trading partners.
13. The Ministers emphasised that ensuring energy security is a crucial foundation for economic development, social stability, national security, and the welfare of all nations worldwide. They called for resilient global supply chains and predictable, stable energy demand to ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy sources. They also stressed the importance of enhancing energy security and market stability by strengthening value chains, promoting open, transparent, and competitive markets, and ensuring the protection of critical energy infrastructure. They strongly condemned all terrorist attacks against critical infrastructure, including critical energy facilities, and against other vulnerable targets.
14. The Ministers reiterated that the objectives, principles and provisions of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and its Paris Agreement, in particular, the principles of common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities (CBDR-RC) in the light of different national circumstances, must be honoured. They reaffirmed their national and joint efforts to promote the implementation of the Paris Agreement In this regard, they stressed the importance of the fulfilment by developed countries of their commitments to provide technology and adequate, predictable, timely, new and additional climate finance that is long overdue to assist developing countries to address climate change. They expressed concern that the goal of developed countries to jointly mobilise USD 100 billion per year by 2020, and annually through 2025, has not been achieved and urged developed countries to meet their commitments. They rejected attempts to link security with the climate change agenda and recalled that the UNFCCC, including the annual Conference of the Parties (COP) sessions, is the appropriate and legitimate international forum to discuss the issue of climate change in all its dimensions.
15. The Ministers emphasised their determination to contribute to a successful COP28 in Dubai, later this year, with the focus on implementation. As the main mechanism for promoting implementation and climate action on all aspects of the Paris Agreement under the UNFCCC, the Global Stocktake must be effective in assessing and identifying implementation gaps on the global response to climate change, whilst prospectively laying the foundations for enhanced ambition by all, in particular by developed countries, and for the fulfilment of outstanding gaps in means of implementation for mitigation and adaptation actions in developing countries.
16. The Ministers welcomed Brazil’s candidacy to host COP30 as the year 2025 will be key to the very future of the global response to climate change.
17. The Ministers recognised the importance of the inclusion of women in peace processes including in conflict prevention and resolution, peacebuilding, post-conflict reconstruction and development, and sustaining peace.
18. The Ministers recalled their national positions concerning the situation in and around Ukraine as expressed at the appropriate fora, including the UNSC and UNGA. They noted with appreciation relevant proposals of mediation and good offices aimed at peaceful resolution of the conflict through dialogue and diplomacy. They called for the full and effective implementation of both the Black Sea Grain Initiative and the Memorandum of Understanding between the Russian Federation and the Secretariat of the United Nations on promoting Russian food products and fertilizers to the world markets and stress the importance of allowing grains and fertilisers to continue to reach those most in need.
19. The Ministers expressed serious concern over continued conflicts in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region and endorsed the Joint Statement by BRICS Deputy Foreign Ministers and Special Envoys at their meeting of 26 April 2023.
20. The Ministers welcomed the readmission of the Syrian Arab Republic to the League of Arab States on 7 May 2023 and reaffirmed their support to all efforts conducive to a political and negotiated solution that respects Syrian sovereignty and territorial integrity.
21. The Ministers expressed concern about the outbreak of violence in Sudan. They urged the immediate cessation of hostilities and they called for the unimpeded access of the Sudanese population to humanitarian assistance. They welcomed the efforts of the African Union, the Intergovernmental Authority for Development, the League of Arab States, the United Nations and its Security Council in seeking solutions for the ongoing crisis. They further welcomed support rendered by various countries, international organisations and agencies in the evacuation of foreign citizens from Sudan.
22. The Ministers expressed strong condemnation of terrorism in all its forms and manifestations whenever, wherever and by whomsoever committed. They recognised the threat emanating from terrorism, extremism conducive to terrorism and radicalisation. They are committed to combating terrorism in all its forms and manifestations, including the cross-border movement of terrorists, and terrorism financing networks and safe havens. They reiterated that terrorism should not be associated with any religion, nationality, civilisation or ethnic group. They reaffirmed their unwavering commitment to contribute further to the global efforts of preventing and countering the threat of terrorism on the basis of respect for international law, in particular the Charter of the United Nations, and human rights, emphasising that States have the primary responsibility in combating terrorism with the United Nations continuing to play central and coordinating role in this area. They also stressed the need for a comprehensive approach of the whole international community to effectively curb the terrorist activities, which pose a serious threat, including in the present-day pandemic environment. The Ministers rejected double standards in countering terrorism and extremism conducive to terrorism. The Ministers called for an expeditious finalisation and adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism within the UN framework and for launching multilateral negotiations on an international convention for the suppression of acts of chemical and biological terrorism, at the Conference of Disarmament. They welcomed the activities of the BRICS Counter-Terrorism Working Group and its five Subgroups based upon the BRICS Counter-Terrorism Strategy and the BRICS Counter-Terrorism Action Plan. We also look forward to further deepening counter-terrorism cooperation.
23. They expressed the need to comprehensively strengthen mechanisms for countering the increased use, in a globalised society, by terrorists and their supporters of emerging and evolving technologies such as Unmanned Aerial Systems, the Internet and other information and communications technologies, including social media platforms, for terrorist purposes, such as for recruitment and incitement to commit terrorist acts, as well as for the financing, planning, and preparation of their activities.
24. The Ministers called for strengthening the system of arms control, disarmament and non-proliferation, including the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction (BTWC) and the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on Their Destruction (CWC), and for preserving their integrity and effectiveness to maintain global stability and international peace and security. They underlined the need to comply with and strengthen the BTWC, including by adopting a legally binding Protocol to the Convention that provides for, inter alia, an efficient verification mechanism. The Ministers reasserted their support for ensuring the long-term sustainability of outer space activities and prevention of an arms race in outer space (PAROS) and of its weaponization, including through negotiations to adopt a relevant legally binding multilateral instrument. They recognised the value of the updated Draft Treaty on the Prevention of the Placement of Weapons in Outer Space, the Threat or Use of Force against Outer Space Objects (PPWT) submitted to the Conference on Disarmament in 2014. They stressed that practical Transparency and Confidence-Building Measures (TCBMs), may also contribute to PAROS.
25. The Ministers, while emphasising the formidable potential of the ICTs for growth and development, recognised new associated possibilities they bring for criminal activities and threats, and expressed concern over the rising level and complexity of criminal misuse of ICTs. They welcomed the ongoing work in the Ad Hoc Committee to elaborate a comprehensive international convention on countering the use of ICTs for criminal purposes and reaffirmed their commitment to cooperating in the implementation of the mandate adopted by the UN General Assembly resolution 75/282 in a timely manner.
26. In line with paragraph 57 of the Beijing Declaration, the Ministers emphasised the responsible and ethical development and use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for socio-economic development and inclusive growth of all societies. They supported communication and cooperation on AI technology to promote mutual benefits, called for strengthening AI international governance and encourage policy exchanges and dialogues on AI, with a view to exploring to establish an effective global governance framework with the aim to protect human rights and spur innovation and economic growth.
27. The Ministers reiterated the need for all countries to cooperate in promoting and protecting human rights and fundamental freedoms under the principles of equality and mutual respect. They agreed to continue to treat all human rights, including the right to development, in a fair and equal manner, on the same footing and with the same emphasis. They agreed to strengthen cooperation on issues of common interests both within BRICS and in multilateral fora including the United Nations General Assembly and Human Rights Council, taking into account the necessity to promote, protect and fulfil human rights in a non-selective, non-politicised and constructive manner and without double standards.
28. The Ministers noted the Chair’s internal report on BRICS Institutional Development in line with paragraphs 71 to 73 of the Beijing Declaration.
29. The Ministers welcomed the Friends of BRICS Foreign Ministers meeting on 2 June 2023.
30. The Ministers expressed their full support to South Africa’s BRICS Chairship in 2023 under the theme “BRICS and Africa: Partnership for Mutually Accelerated Growth, Sustainable Development, and Inclusive Multilateralism”. They expressed their commitment to working together to ensure the success of the XV BRICS Summit. The Ministers looked forward to the next BRICS Ministers of Foreign Affairs and International Relations meeting to be held on the margins of UNGA78 and hosted by the Russian Federation as the incoming Chair of BRICS in 2024.

This analytical report on the perils of US hegemony was released by China on the 20th of February 2023. It is evident that much of the world is now alienated by the USA and the West. This is particularly so after the Ukraine-Russia conflict that erupted a year ago. The majority of the world remains non-commital but certainly does not support the US or Ukraine in this conflict nor do they condemn Russia. In effect, the non-western world has openly indicated that this unnecessary war is caused by the aggressive actions of NATO and the US to provoke Russia. The constant interventions and wars waged by the US and NATO in the name of democracy and disregarding the UN are now being questioned. China has cleverly utilised this sentiment to time its publication. The paper is very well analysed, crisply argued, and has flagged real questions to the world community. In short, the paper implies that the US and its allies pose the gravest threat to global stability and peace, and more so to the sovereignty of all countries.
This paper was published earlier in fmprc.gov.cn

Introduction
Since becoming the world’s most powerful country after the two world wars and the Cold War, the United States has acted more boldly to interfere in the internal affairs of other countries, pursue, maintain and abuse hegemony, advance subversion and infiltration, and willfully wage wars, bringing harm to the international community.
The United States has developed a hegemonic playbook to stage “colour revolutions,” instigate regional disputes and even directly launch wars under the guise of promoting democracy, freedom and human rights. Clinging to the Cold War mentality, the United States has ramped up bloc politics and stoked conflict and confrontation. It has overstretched the concept of national security, abused export controls and forced unilateral sanctions upon others. It has taken a selective approach to international law and rules, utilizing or discarding them as it sees fit, and has sought to impose rules that serve its own interests in the name of upholding a “rules-based international order.”
This report, by presenting the relevant facts, seeks to expose the U.S. abuse of hegemony in the political, military, economic, financial, technological and cultural fields and to draw greater international attention to the perils of the U.S. practices to world peace and stability and the well-being of all peoples.
I. Political Hegemony – Throwing Its Weight Around
The United States has long been attempting to mould other countries and the world order with its own values and political system in the name of promoting democracy and human rights.
◆ Instances of U.S. interference in other countries’ internal affairs abound. In the name of “promoting democracy,” the United States practised a “Neo-Monroe Doctrine” in Latin America, instigated “colour revolutions” in Eurasia, and orchestrated the “Arab Spring” in West Asia and North Africa, bringing chaos and disaster to many countries.
In 1823, the United States announced the Monroe Doctrine. While touting an “America for the Americans,” what it truly wanted was an “America for the United States.”
Since then, the policies of successive U.S. governments toward Latin America and the Caribbean Region have been riddled with political interference, military intervention and regime subversion. From its 61-year hostility toward and blockade of Cuba to its overthrow of the Allende government of Chile, U.S. policy on this region has been built on one maxim-those who submit will prosper; those who resist shall perish.
The year 2003 marked the beginning of a succession of “colour revolutions” – the “Rose Revolution” in Georgia, the “Orange Revolution” in Ukraine and the “Tulip Revolution” in Kyrgyzstan. The U.S. Department of State openly admitted playing a “central role” in these “regime changes.” The United States also interfered in the internal affairs of the Philippines, ousting President Ferdinand Marcos Sr. in 1986 and President Joseph Estrada in 2001 through the so-called “People Power Revolutions.”
In January 2023, former U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo released his new book Never Give an Inch: Fighting for the America I Love. He revealed in it that the United States had plotted to intervene in Venezuela. The plan was to force the Maduro government to reach an agreement with the opposition, deprive Venezuela of its ability to sell oil and gold for foreign exchange, exert high pressure on its economy, and influence the 2018 presidential election.
◆ The U.S. exercises double standards on international rules. Placing its self-interest first, the United States has walked away from international treaties and organizations and put its domestic law above international law. In April 2017, the Trump administration announced that it would cut off all U.S. funding to the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) with the excuse that the organization “supports, or participates in the management of a program of coercive abortion or involuntary sterilization.” The United States quit UNESCO twice in 1984 and 2017. In 2017, it announced leaving the Paris Agreement on climate change. In 2018, it announced its exit from the UN Human Rights Council, citing the organization’s “bias” against Israel and failure to protect human rights effectively. In 2019, the United States announced its withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty to seek the unfettered development of advanced weapons. In 2020, it announced pulling out of the Treaty on Open Skies.
The United States has also been a stumbling block to biological arms control by opposing negotiations on a verification protocol for the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) and impeding international verification of countries’ activities relating to biological weapons. As the only country in possession of a chemical weapons stockpile, the United States has repeatedly delayed the destruction of chemical weapons and remained reluctant in fulfilling its obligations. It has become the biggest obstacle to realizing “a world free of chemical weapons.”
◆ The United States is piecing together small blocs through its alliance system. It has been forcing an “Indo-Pacific Strategy” onto the Asia-Pacific region, assembling exclusive clubs like the Five Eyes, the Quad and AUKUS, and forcing regional countries to take sides. Such practices are essentially meant to create division in the region, stoke confrontation and undermine peace.
◆ The U.S. arbitrarily passes judgment on democracy in other countries and fabricates a false narrative of “democracy versus authoritarianism” to incite estrangement, division, rivalry and confrontation. In December 2021, the United States hosted the first “Summit for Democracy,” which drew criticism and opposition from many countries for making a mockery of the spirit of democracy and dividing the world. In March 2023, the United States will host another “Summit for Democracy,” which remains unwelcome and will again find no support.
II. Military Hegemony – Wanton Use of Force
The history of the United States is characterized by violence and expansion. Since it gained independence in 1776, the United States has constantly sought expansion by force: it slaughtered Indians, invaded Canada, waged a war against Mexico, instigated the American-Spanish War, and annexed Hawaii. After World War II, the wars either provoked or launched by the United States included the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Gulf War, the Kosovo War, the War in Afghanistan, the Iraq War, the Libyan War and the Syrian War, abusing its military hegemony to pave the way for expansionist objectives. In recent years, the U.S. average annual military budget has exceeded $700 billion, accounting for 40 percent of the world’s total, more than the 15 countries behind it combined. The United States has about 800 overseas military bases, with 173,000 troops deployed in 159 countries.
According to the book America Invades: How We’ve Invaded or been Militarily Involved with almost Every Country on Earth, the United States has fought or been militarily involved with almost all the 190-odd countries recognized by the United Nations with only three exceptions. The three countries were “spared” because the United States did not find them on the map.
◆ As former U.S. President Jimmy Carter put it, the United States is undoubtedly the most warlike nation in the history of the world. According to a Tufts University report, “Introducing the Military Intervention Project: A new Dataset on U.S. Military Interventions, 1776-2019,” the United States undertook nearly 400 military interventions globally between those years, 34 percent of which were in Latin America and the Caribbean, 23 percent in East Asia and the Pacific, 14 percent in the Middle East and North Africa, and 13 percent in Europe. Currently, its military intervention in the Middle East and North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa is on the rise.
Alex Lo, a South China Morning Post columnist, pointed out that the United States has rarely distinguished between diplomacy and war since its founding. It overthrew democratically elected governments in many developing countries in the 20th century and immediately replaced them with pro-American puppet regimes. Today, in Ukraine, Iraq, Afghanistan, Libya, Syria, Pakistan and Yemen, the United States is repeating its old tactics of waging proxy, low-intensity, and drone wars.
◆ U.S. military hegemony has caused humanitarian tragedies. Since 2001, the wars and military operations launched by the United States in the name of fighting terrorism have claimed over 900,000 lives, with some 335,000 of them civilians, injured millions and displaced tens of millions. The 2003 Iraq War resulted in some 200,000 to 250,000 civilian deaths, including over 16,000 directly killed by the U.S. military, and left more than a million homeless.
The United States has created 37 million refugees around the world. Since 2012, the number of Syrian refugees alone has increased tenfold. Between 2016 and 2019, 33,584 civilian deaths were documented in the Syrian fighting, including 3,833 killed by U.S.-led coalition bombings, half of them women and children. The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) reported on November 9, 2018, that the air strikes launched by U.S. forces on Raqqa alone killed 1,600 Syrian civilians.
The two-decade-long war in Afghanistan devastated the country. A total of 47,000 Afghan civilians and 66,000 to 69,000 Afghan soldiers and police officers unrelated to the September 11 attacks were killed in U.S. military operations, and more than 10 million people were displaced. The war in Afghanistan destroyed the foundation of economic development there and plunged the Afghan people into destitution. After the “Kabul debacle” in 2021, the United States announced that it would freeze some 9.5 billion dollars in assets belonging to the Afghan central bank, a move considered “pure looting.”
In September 2022, Turkish Interior Minister Suleyman Soylu commented at a rally that the United States has waged a proxy war in Syria, turned Afghanistan into an opium field and heroin factory, thrown Pakistan into turmoil, and left Libya in incessant civil unrest. The United States does whatever it takes to rob and enslave the people of any country with underground resources.
The United States has also adopted appalling methods in war. During the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Gulf War, the Kosovo War, the War in Afghanistan and the Iraq War, the United States used massive quantities of chemical and biological weapons as well as cluster bombs, fuel-air bombs, graphite bombs and depleted uranium bombs, causing enormous damage on civilian facilities, countless civilian casualties and lasting environmental pollution.
III. Economic Hegemony – Looting and Exploitation
After World War II, the United States led efforts to set up the Bretton Woods System, the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank, which, together with the Marshall Plan, formed the international monetary system centred around the U.S. dollar. In addition, the United States has established institutional hegemony in the international economic and financial sector by manipulating the weighted voting systems, rules and arrangements of international organizations, including “approval by 85 percent majority” and its domestic trade laws and regulations. By taking advantage of the dollar’s status as the major international reserve currency, the United States is basically collecting “seigniorage” from around the world; and using its control over international organizations, it coerces other countries into serving America’s political and economic strategy.
◆ The United States exploits the world’s wealth with the help of “seigniorage.” It costs only about 17 cents to produce a $100 bill, but other countries had to pony up $100 worth of actual goods in order to obtain one. It was pointed out more than half a century ago that the United States enjoyed exorbitant privilege and deficit without tears created by its dollar and used the worthless paper note to plunder the resources and factories of other nations.
◆ The hegemony of the U.S. dollar is the main source of instability and uncertainty in the world economy. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States abused its global financial hegemony and injected trillions of dollars into the global market, leaving other countries, especially emerging economies, to pay the price. In 2022, the Fed ended its ultra-easy monetary policy and turned to aggressive interest rate hikes, causing turmoil in the international financial market and substantial depreciation of other currencies, such as the euro, many of which dropped to a 20-year low. As a result, a large number of developing countries were challenged by high inflation, currency depreciation and capital outflows. This was exactly what Nixon’s secretary of the treasury, John Connally, once remarked, with self-satisfaction yet sharp precision, “The dollar is our currency, but it is your problem.”
◆ With its control over international economic and financial organizations, the United States imposes additional conditions for assisting other countries. In order to reduce obstacles to U.S. capital inflow and speculation, the recipient countries are required to advance financial liberalization and open up financial markets so that their economic policies would fall in line with America’s strategy. According to the Review of International Political Economy, along with the 1,550 debt relief programs extended by the IMF to its 131 member countries from 1985 to 2014, as many as 55,465 additional political conditions had been attached.
◆ The United States willfully suppresses its opponents with economic coercion. In the 1980s, to eliminate the economic threat posed by Japan and control and use the latter in service of America’s strategic goal of confronting the Soviet Union and dominating the world, the United States leveraged its hegemonic financial power against Japan and concluded the Plaza Accord. As a result, the yen was pushed up, and Japan was pressed to open up its financial market and reform its financial system. The Plaza Accord dealt a heavy blow to the growth momentum of the Japanese economy, leaving Japan to what was later called “three lost decades.”
◆ America’s economic and financial hegemony has become a geopolitical weapon. Doubling down on unilateral sanctions and “long-arm jurisdiction,” the United States has enacted such domestic laws as the International Emergency Economic Powers Act, the Global Magnitsky Human Rights Accountability Act, and the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act, and introduced a series of executive orders to sanction specific countries, organizations or individuals. Statistics show that U.S. sanctions against foreign entities increased by 933 percent from 2000 to 2021. The Trump administration alone has imposed more than 3,900 sanctions, which means three sanctions per day. So far, the United States had or has imposed economic sanctions on nearly 40 countries across the world, including Cuba, China, Russia, the DPRK, Iran and Venezuela, affecting nearly half of the world’s population. “The United States of America” has turned itself into “the United States of Sanctions.” And “long-arm jurisdiction” has been reduced to nothing but a tool for the United States to use its means of state power to suppress economic competitors and interfere in normal international business. This is a serious departure from the principles of a liberal market economy that the United States has long boasted.
IV. Technological Hegemony – Monopoly and Suppression
The United States seeks to deter other countries’ scientific, technological and economic development by wielding monopoly power, suppression measures and technology restrictions in high-tech fields.
◆ The United States monopolizes intellectual property in the name of protection. Taking advantage of the weak position of other countries, especially developing ones, on intellectual property rights and the institutional vacancy in relevant fields, the United States reaps excessive profits through monopoly. In 1994, the United States pushed forward the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), forcing the Americanized process and standards in intellectual property protection in an attempt to solidify its monopoly on technology.
In the 1980s, to contain the development of Japan’s semiconductor industry, the United States launched the “301” investigation, built bargaining power in bilateral negotiations through multilateral agreements, threatened to label Japan as conducting unfair trade, and imposed retaliatory tariffs, forcing Japan to sign the U.S.-Japan Semiconductor Agreement. As a result, Japanese semiconductor enterprises were almost completely driven out of global competition, and their market share dropped from 50 percent to 10 percent. Meanwhile, with the support of the U.S. government, a large number of U.S. semiconductor enterprises took the opportunity and grabbed a larger market share.
◆ The United States politicizes and weaponizes technological issues and uses them as ideological tools. Overstretching the concept of national security, the United States mobilized state power to suppress and sanction Chinese company Huawei, restricted the entry of Huawei products into the U.S. market, cut off its supply of chips and operating systems, and coerced other countries to ban Huawei from undertaking local 5G network construction. It even talked Canada into unwarrantedly detaining Huawei’s CFO, Meng Wanzhou, for nearly three years.
The United States has fabricated a slew of excuses to clamp down on China’s high-tech enterprises with global competitiveness and has put more than 1,000 Chinese enterprises on sanction lists. In addition, the United States has also imposed controls on biotechnology, artificial intelligence and other high-end technologies, reinforced export restrictions, tightened investment screening, suppressed Chinese social media apps such as TikTok and WeChat, and lobbied the Netherlands and Japan to restrict exports of chips and related equipment or technology to China.
The United States has also practised double standards in its policy on China-related technological professionals. To sideline and suppress Chinese researchers, since June 2018, visa validity has been shortened for Chinese students majoring in certain high-tech-related disciplines, repeated cases have occurred where Chinese scholars and students going to the United States for exchange programs and study were unjustifiably denied and harassed, and large-scale investigation on Chinese scholars working in the United States was carried out.
◆ The United States solidifies its technological monopoly in the name of protecting democracy. By building small blocs of technology, such as the “chips alliance” and “clean network,” the United States has put “democracy” and “human rights” labels on high technology and turned technological issues into political and ideological issues to fabricate excuses for its technological blockade against other countries. In May 2019, the United States enlisted 32 countries to the Prague 5G Security Conference in the Czech Republic and issued the Prague Proposal in an attempt to exclude China’s 5G products. In April 2020, then U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo announced the “5G clean path,” a plan designed to build a technological alliance in the 5G field with partners bonded by their shared ideology on democracy and the need to protect “cyber security.” The measures, in essence, are the U.S. attempts to maintain its technological hegemony through technological alliances.
◆ The United States abuses its technological hegemony by carrying out cyberattacks and eavesdropping. The United States has long been notorious as an “empire of hackers,” blamed for its rampant acts of cyber theft around the world. It has all kinds of means to enforce pervasive cyberattacks and surveillance, including using analogue base station signals to access mobile phones for data theft, manipulating mobile apps, infiltrating cloud servers, and stealing through undersea cables. The list goes on.
U.S. surveillance is indiscriminate. All can be targets of its surveillance, be they rivals or allies, even leaders of allied countries such as former German Chancellor Angela Merkel and several French Presidents. Cyber surveillance and attacks launched by the United States, such as “Prism,” “Dirtbox,” “Irritant Horn” and “Telescreen Operation,” are all proof that the United States is closely monitoring its allies and partners. Such eavesdropping on allies and partners has already caused worldwide outrage. Julian Assange, the founder of Wikileaks, a website that has exposed U.S. surveillance programs, said, “Do not expect a global surveillance superpower to act with honour or respect. There is only one rule: There are no rules.”
V. Cultural Hegemony – Spreading False Narratives
The global expansion of American culture is an important part of its external strategy. The United States has often used cultural tools to strengthen and maintain its hegemony in the world.
◆ The United States embeds American values in its products, such as movies. American values and lifestyle are tied to its movies, TV shows, publications, media content and programs by government-funded non-profit cultural institutions. It thus shapes a cultural and public opinion space in which American culture reigns and maintains cultural hegemony. In his article “The Americanization of the World,” John Yemma, an American scholar, exposed the real weapons in U.S. cultural expansion, Hollywood, the image design factories on Madison Avenue and the production lines of Mattel Company and Coca-Cola.
There are various vehicles the United States uses to keep its cultural hegemony. American movies are the most used; they now occupy more than 70 percent of the world’s market share. The United States skillfully exploits its cultural diversity to appeal to various ethnicities. When Hollywood movies descend on the world, they scream the American values tied to them.
◆ American cultural hegemony not only shows itself in “direct intervention” but also in “media infiltration” and as “a trumpet for the world.” U.S.-dominated Western media has a particularly important role in shaping global public opinion in favour of U.S. meddling in the internal affairs of other countries.
The U.S. government strictly censors all social media companies and demands their obedience. Twitter CEO Elon Musk admitted on December 27, 2022, that all social media platforms work with the U.S. government to censor content, reported Fox Business Network. Public opinion in the United States is subject to government intervention to restrict all unfavourable remarks. Google often makes pages disappear.
The U.S. Department of Defense manipulates social media. In December 2022, The Intercept, an independent U.S. investigative website, revealed that in July 2017, U.S. Central Command official Nathaniel Kahler instructed Twitter’s public policy team to augment the presence of 52 Arabic-language accounts on a list he sent, six of which were to be given priority. One of the six was dedicated to justifying U.S. drone attacks in Yemen, such as by claiming that the attacks were precise and killed only terrorists, not civilians. Following Kahler’s directive, Twitter put those Arabic-language accounts on a “white list” to amplify certain messages.
◆The United States practices double standards on the freedom of the press. It brutally suppresses and silences the media of other countries by various means. The United States and Europe bar mainstream Russian media, such as Russia Today and Sputnik, from their countries. Platforms such as Twitter, Facebook and YouTube openly restrict official accounts of Russia. Netflix, Apple and Google have removed Russian channels and applications from their services and app stores. Unprecedented draconian censorship is imposed on Russia-related content.
◆The United States abuses its cultural hegemony to instigate “peaceful evolution” in socialist countries. It sets up news media and cultural outfits targeting socialist countries. It pours staggering amounts of public funds into radio and TV networks to support their ideological infiltration, and these mouthpieces bombard socialist countries in dozens of languages with inflammatory propaganda day and night.
The United States uses misinformation as a spear to attack other countries and has built an industrial chain around it; there are groups and individuals making up stories and peddling them worldwide to mislead public opinion with the support of nearly limitless financial resources.
Conclusion
While a just cause wins its champion-wide support, an unjust one condemns its pursuer to be an outcast. The hegemonic, domineering, and bullying practices of using strength to intimidate the weak, taking from others by force and subterfuge, and playing zero-sum games are exerting grave harm. The historical trends of peace, development, cooperation and mutual benefit are unstoppable. The United States has been overriding truth with its power and trampling justice to serve self-interest. These unilateral, egoistic and regressive hegemonic practices have drawn growing, intense criticism and opposition from the international community.
Countries need to respect each other and treat each other as equals. Big countries should behave in a manner befitting their status and take the lead in pursuing a new model of state-to-state relations featuring dialogue and partnership, not confrontation or alliance. China opposes all forms of hegemonism and power politics and rejects interference in other countries internal affairs. The United States must conduct serious soul-searching. It must critically examine what it has done, let go of its arrogance and prejudice, and quit its hegemonic, domineering and bullying practices.
Feature Image: Photograph by M Matheswaran
Cartoon: canadiandimensions.com Caricature showing Uncle Sam lecturing four children labelled Phillippines (who appears similar to Phillippine leader Emilio Aguinaldo), Hawaii, Porto (sic) Rio, and Cuba in front of children holding books labelled with various US states. In the background are an American Indian holding a book upside down, a Chinese boy at the door and a black boy cleaning the window. Originally published on p. 8-9 of the January 25, 1899 issue of Puck magazine.

[powerkit_button size=”lg” style=”info” block=”true” url=”https://admin.thepeninsula.org.in/2022/03/29/tpf-analysis-series-on-russia-ukraine-conflict/” target=”_blank” nofollow=”false”]
The First Paper of the Series – TPF Analysis Series on Russia – Ukraine Conflict #1
[/powerkit_button]
In a press conference marking his first year in office, President Biden, on the question of Russia invading Ukraine, remarked that such an event would, “be the most consequential thing that’s happened in the world, in terms of war and peace, since World War Two”. [1] It has now been two months since Russia officially launched its “special military operation” in Ukraine, which the US and its allies consider an unjustified invasion of a sovereign state. The conflict in the Eurasian continent has drawn global attention to Europe and US-Russia tensions have ratcheted to levels that were prevalent during the Cold War. The conflict has also raised pertinent questions on understanding what exactly are Russian stakes in Ukraine and the latter’s role in the evolving security architecture of Europe. The second paper in this series will delve into these questions.
The current Russian position stems from the experience that Russia, and Putin, gained while dealing with the West on a host of issues, not least of which was NATO expansion.
The Ties that Bind
An examination of post-Soviet history reveals that Russian preoccupation with security threats from NATO is not embedded in Russian geopolitics; instead, it has been reported that, early on, Russia was even agreeable to joining the military alliance. The current Russian position stems from the experience that Russia, and Putin, gained while dealing with the West on a host of issues, not least of which was NATO expansion. A line of argument sympathetic to Russia is President Putin’s contention that terms dictated to Russia during the post-Cold War settlements were unfair. The claim is a reference to Secretary of State James Baker’s statement on the expansion of NATO, “not an inch of NATO’s present military jurisdiction will spread in an eastern direction”, in 1990 in a candid conversation with Mikhael Gorbachev on the matter of reunification of Germany. [2] It could be argued that it is this commitment and subsequent violation through expansions of NATO is one of the main causes of the current conflict.
At the root of the problem was Russia’s security concerns – regarding both traditional and hybrid security – that ultimately led to the centralisation of power after a democratic stint under Yeltsin. Accordingly, Putin had put it in late 1999, “A strong state for Russia is not an anomaly, or something that should be combated, but, on the contrary, the source and guarantor of order, the initiator and the main driving force of any changes”. [3]
Historically being a land power, Russia has viewed Ukraine as a strategically critical region in its security matrix. However, as the central control of Moscow weakened in the former USSR, the nationalist aspirations of the Ukrainian people began to materialise and Ukraine played a crucial role, along with the Russian Federation and Belarus, in dissolving the former Soviet Union. The two countries found themselves on opposite sides on extremely fundamental issues, such as security, economic partnership, post-Soviet order, and, not least, sovereignty. In Belovezh, in early December of 1991, when Russian President Boris Yeltsin, Ukrainian President Leonid Kravchuk and Belarusian leader Stanislav Shushkevich met to dissolve the USSR, major disagreements regarding the transitional phase and future of the republics erupted. Yeltsin expressed his desire for some sort of central control of the republics, whereas Kravchuk was vehemently opposed to any arrangement that might compromise his country’s sovereignty. Later, at the foundational ceremony of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), he stressed a common military, the most potent rejection of which came from Kravchuk. [4]
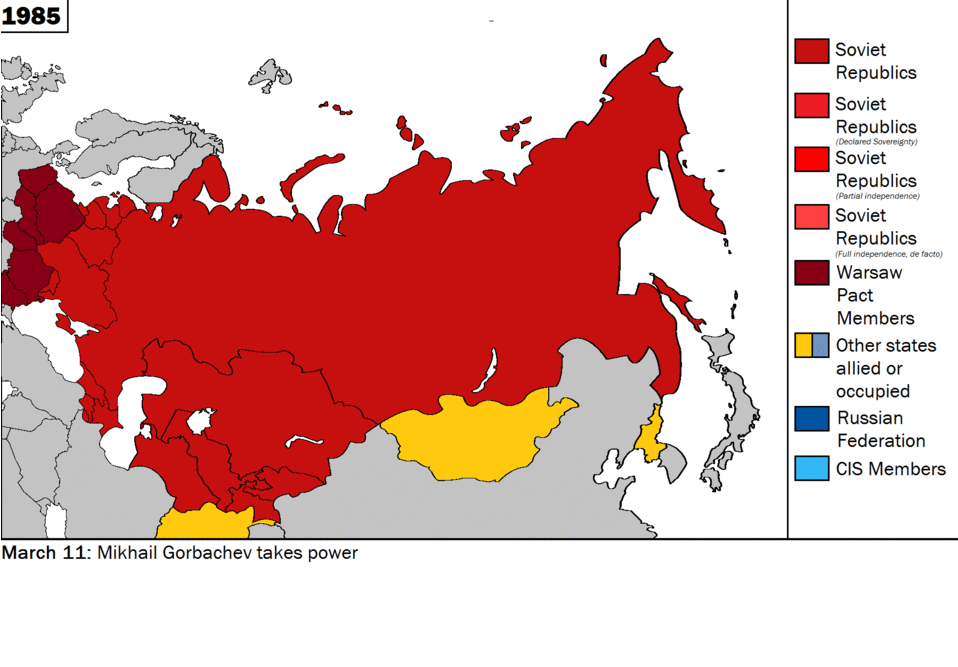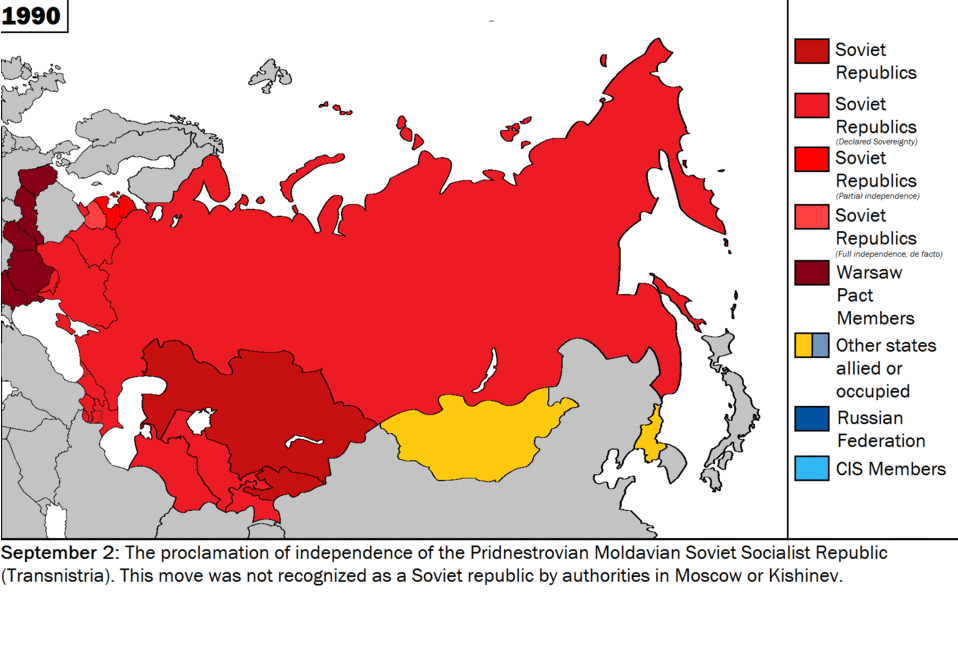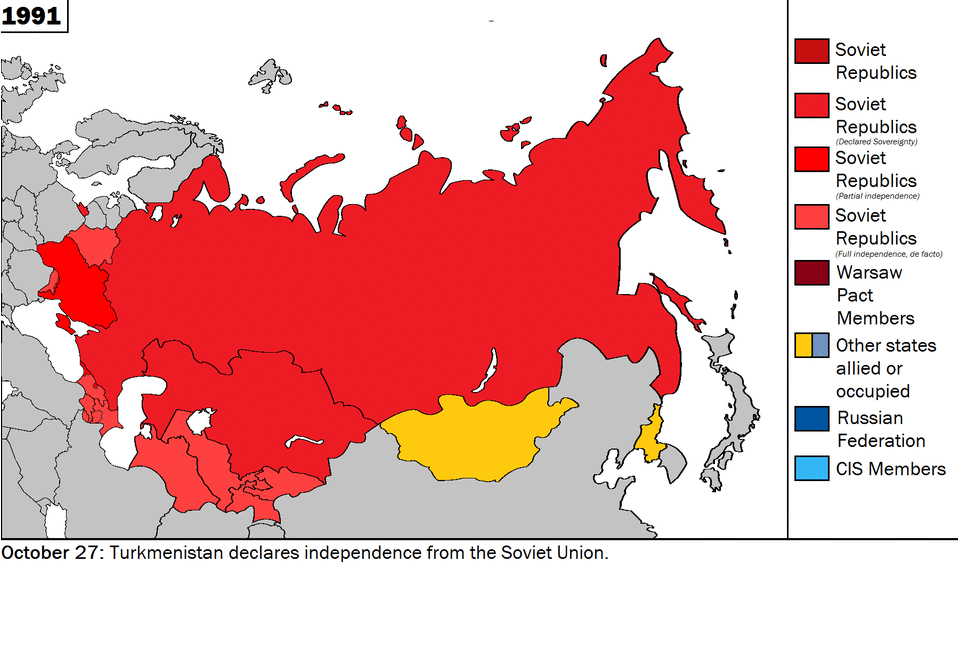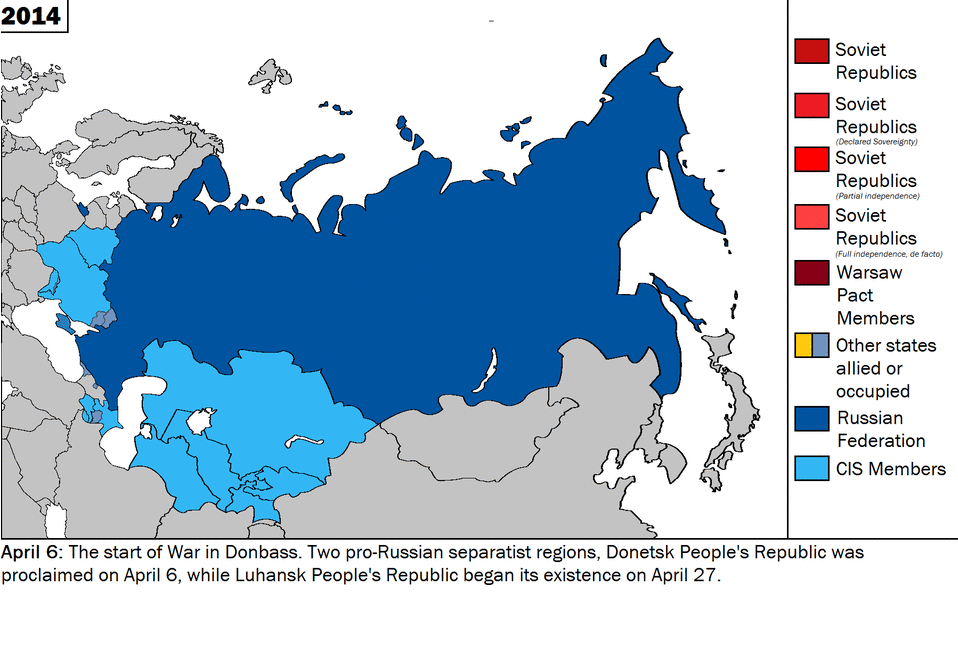
Source: Wikimedia Commons
The elephant in the room, however, was the status of Sevastopol, which housed the headquarters of the Black Sea Fleet. Yeltsin was quoted saying that “The Black Sea Fleet was, is and will be Russia’s. No one, not even Kravchuk will take it away from Russia”. [5] Though the issue was soon temporarily resolved –with the two countries dividing the fleet equally amongst themselves, it continued to dominate and sour their relationship. Russia, as the successor state of the USSR, wanted the base and the entire fleet in its navy. Yeltsin even offered gas at concessional rates to Ukraine if it handed over the city and nuclear weapons to Russia. The issue remained unresolved until the 1997 Friendship Treaty under which Ukraine granted Moscow the entire fleet and leased Sevastopol to Russia until 2017 (later extended).
Ukraine, under Kravchuk and, later, Leonid Kuchma, struggled to tread a tightrope between Russia and the European Union. On one hand, it was economically knit with former Soviet Republics, and on the other, it was actively looking to get economic benefits from the EU. However, soon a slide towards the west was conspicuous. In 1994, it preferred a Partnership and Cooperation Agreement with the EU over CIS Customs Union, which was a Russian initiative. Later, in 1996, it declined to join a new group consisting of former Soviet Republics ‘On Deepening Integration’, scuttling the initiative, since its purpose was to bring Ukraine back into the Russian fold. [6] By 1998, the Kuchma government had formulated a ‘Strategy of Integration into the European Union’. [7]
Nuclear weapons were another point of contention between the two. Ukraine was extremely reluctant to give up its arsenal, citing security threats from Russia. Kravchuk received a verbal ‘security guarantee’ from the US which forced Russia to “respect the independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity of each nation” [8] in exchange for surrendering Ukraine’s nuclear weapons.
Notwithstanding the disputes, there was a great deal of cooperation between the two, especially after Kuchma’s re-election in 1999. Kuchma’s hook-up with authoritarianism distanced Kyiv from Brussels and brought it closer to Moscow. Ukraine agreed to join Russian initiatives of the Eurasian Economic Community as an observer and Common Economic Space as a full member. At home as well, his support in the eastern parts of the country, where ethnic Russians dwelled, increased dramatically, as evident in the 2002 Parliamentary Elections. [9] However, the bonhomie was soon disrupted by a single event.
The Orange Revolution was Russia’s 9/11. [10] It dramatically altered Russian thinking on democracy and its ties with the West. It raised the prospect in Russia that Ukraine might be lost completely. It further made them believe the colour revolutions in former Soviet republics were CIA toolkits for regime change. More importantly, it made the Russians apprehensive of a similar revolution within their borders. As a result, the distrust between Russia and the West, and Russia and Ukraine grew considerably. As a nationalist, Victor Yushchenko formulated policies that directly hurt Russian interests. The two countries fought ‘Gas Wars’ in 2006 and 2009, which made both the EU and Russia uncomfortable with Ukraine as a gas transit country. Furthermore, Yushchenko bestowed the title of ‘Hero of Ukraine’ upon Stepan Bandera, a Nazi collaborator and perpetrator of the Holocaust, a decision that surely did not go well with Moscow.
Geoeconomics: Ukraine as a Gas Transit Country
The current war is the worst in Europe since the Second World War. Still, Ukraine continues to transit Russian gas through its land, Russia continues to pay for it, and Western Europe continues to receive the crucial resource. The war has shattered all the big bets on Russian dependence on Ukraine for delivering gas to Western Europe and has renewed the discourse on reducing European energy dependence on Russia. Since the EU imports 40% of its gas from Russia, almost a quarter of which flows through Ukraine, Kyiv has had leverage in dealing with Russians in the past. It has been able to extract favourable terms by either stopping or diverting gas for its own domestic use at a time of heightened tensions between Ukraine and Russia. As a result, the EU was directly drawn into the conflict between them, infructuating Moscow’s pressure tactics for a long.
Moscow has made numerous attempts in the past to bypass Ukraine by constructing alternate pipelines. Nord Stream, the most popular of them, was conceived in 1997, as an attempt to decrease the leverage of the transit states. The pipeline was described as the “Molotov-Ribbentrop Pipeline” by Polish Defence Minister Radoslaw Sirkosi for the geoeconomic influence it gave to Russia. [11] Another project – the South Stream – was aimed at providing gas to the Balkans, and through it to Austria and Italy. The pipeline was conceived in the aftermath of the Orange Revolution and its construction was motivated by geoeconomics, rather than economic viability. It would have led to Russia bypassing Ukraine in delivering gas to the Balkans and Central Europe, thus seizing its significant leverage, and relegating it to vulnerable positions in which Moscow could have eliminated the gas subsidies Ukraine was being provided. [12]As a result of economic unviability, the project was abandoned in 2014.
To a certain extent, the European Union has been complicit in making matters worse for Russia. For instance, during the 2009 ‘Gas War’ – that began due to Ukraine’s non-payment of gas debt to Russia – instead of holding Ukraine accountable, the EU countries blamed Russia for the gas crisis in Europe and asked Russia to resume gas supply to Ukraine. Later, realising the importance of Ukraine as a transit country, it reached an agreement with Kyiv that “recognized the importance of the further expansion and modernization of Ukraine’s gas transit system as an indispensable pillar of the common European energy infrastructure, and the fact that Ukraine is a strategic partner for the EU gas sector”. The agreement excluded Russia as a party, which saw it as undermining the collaboration between itself and Ukraine, and injuring its influence on the country. [13] The Russian grievance becomes even more palpable when we view the significant gas subsidies it has provided to Ukraine for more than two decades.
Similarly, the EU countries viewed Nord Stream 2 from a geostrategic and geo-economic perspective. In December last year, German Economic Affairs Minister Robert Habeck warned Russia of halting Nord Stream 2 if it attacks Ukraine. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz was quoted saying that he would do ‘anything’ to ensure that Ukraine remains a transit country for Russian gas. [14] In fact, the pipeline – that is set to double the capacity of gas delivered to the EU – has faced opposition from almost all Western European countries, the US, the EU as well as Ukraine, which has described it as ‘A dangerous Geopolitical Weapon’. [15] The pipeline had raised concerns amongst Ukrainians of losing a restraining factor on Moscow’s behaviour. [16] However, with the pipeline still inoperable, the Kremlin has already made the restraining factor ineffective.
The Security Objective
The Russian Federation is a country which spreads from the European Continent to Asia. In this giant nation, the hospitable region where people live is mainly on the European side, which also comprises main cities like St. Petersburg, Volgograd and the Capital City Moscow. Throughout history, Russia has seen invasions by Napoleon as well as Hitler, and the main area through which these invasions and wars happened was through Ukrainian land which gave them direct access to Russia – due to the lack of any geographical barriers. It was certainly a contributing factor towards the initial success of these invasions. Today, we might understand these events as Russia’s sense of vulnerability and insecurity if history is any indicator.
The Russian Federation also follows a similar approach to ensuring its security, survival and territorial integrity. Russia’s interest in Ukraine is as much geopolitical as cultural. Since Russians and Ukrainians were intrinsically linked through their culture and language, Ukraine quickly came to be seen as Russian land, with Ukrainians being recognized as ‘Little Russians’ (Kubicek, 2008), as compared to the “Great Russians”. They were consequently denied the formation of a distinct Ukrainian identity. Putin gave substance to this sentiment as, according to a US diplomatic cable leak, he had “implicitly challenged the territorial integrity of Ukraine, suggesting that Ukraine was an artificial creation sewn together from the territory of Poland, the Czech Republic, Romania, and especially Russia in the aftermath of the Second World War” during a Russia-NATO Council meeting. [17]
Crimea and much of eastern Ukraine are ethnically Russian and desire closer ties with Russia. But moving further west, the people become increasingly cosmopolitan and it is mostly this population that seeks greater linkage with the Western European countries and membership into the EU and NATO. This in addition to the Euro Maidan protests is what Putin has used to justify the annexation of Crimea in 2014. The other security consideration was the threat it faced from the likelihood of NATO establishing a base in Crimea given its own presence in Sevastopol in the Black Sea.
In the current scenario, the second phase of Russian Military operation in the East and South has shown us the larger vulnerabilities Moscow has which are being countered through control of certain points in the region. By liberating the Donbass region in the east, Russia plans to create a buffer zone between itself and the west to stop future aggression and keep enemies at bay. But the extension of this buffer zone all the way to Odessa is indicative of other strategic considerations. Mariupol in the south of Ukraine is one of the many extended strategic points Russia now controls leading us to ask just why Mariupol is a game-changer in this conflict?
The port city of Mariupol is a small area geographically, but it provides the land bridge for the Russian forces in the Crimean Peninsula to join the Military operation in the Donbas region. Moreover, it gives Russia a land bridge to Crimea from the Russian Mainland. According to General Sir Richard Barrons, former Commander of UK Joint Forces Command, Mariupol is crucial to Russia’s offensive movement, – “When the Russians feel they have successfully concluded that battle, they will have completed a land bridge from Russia to Crimea and they will see this a major strategic success.” [18]

Source: ISW (Assessment on 09 May, 2022)
If the port city of Mariupol is important for the creation of a land corridor, then the Sea of Azov which is adjacent to it is even more important due to its strategic position. [19] The three geopolitical reasons why this sea is important are as follows:
If Mariupol and the Sea of Azov are considered the most important strategically valuable features by Russia, there also exists the crucial points of Kherson and Odessa which will give Russia complete dominance of the Ukrainian coast line, thus giving larger access and control in the Black Sea region that has the potential to be militarised in the future in conflicts with the West. Moreover, it gives Russia a land corridor to Transnistria which is a Pro-Russian separatist area in Moldova and an opening into the Romanian border through Odessa, thus balancing the build-up of NATO forces in the region.
Conclusion
The Ukrainian crisis is as much the West’s doing as Russia’s and an ear sympathetic to the Russian narrative might even say that the West took advantage of Russia when it was vulnerable immediately following the collapse of the Soviet Union in negotiations regarding the German state reunification and NATO enlargement.
The bottom line is that, presently, Putin views NATO as an existential security threat to the Russian state and sees the US and its allies’ support of Ukraine as a challenge. Ukraine’s membership in the EU and NATO is a non-starter for Russia and pitting a Ukraine, that has a symbiotic relationship with Russia at all levels, against a slightly diminished but still formidable great power will have consequences for the security architecture and geopolitics of the region. The Ukrainian crisis is as much the West’s doing as Russia’s and an ear sympathetic to the Russian narrative might even say that the West took advantage of Russia when it was vulnerable immediately following the collapse of the Soviet Union in negotiations regarding the German state reunification and NATO enlargement. On some level, NATO countries recognize the fact that Ukraine and Georgia can never be allowed membership into the North Atlantic alliance because the alternative of wilfully ignoring Russia’s security and national interests is just a recipe for disaster and might just launch the region into the single biggest armed conflict since World War 2.
References:
[1] The White House. (2022, January 20). Remarks by president Biden in the press conference. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2022/01/19/remarks-by-president-biden-in-press-conference-6/
[2] Savranskaya, S., Blanton, T. S., & Zubok, V. (2010). Masterpieces of history: The peaceful end of the Cold War in Europe, 1989. Central European University Press.
[3] Putin, Vladimir. “Rossiya na Rubezhe Tysyacheletii,” Nesavisimaya Gazeta, December 30, 1999, quoted in D’Anieri, Paul (2019). Ukraine and Russia: From Civilized Divorce to Uncivil War. Cambridge University Press.
[4] Ibid
[5] Rettie, J. and James Meek, “Battle for Soviet Navy,” The Guardian, January 10, 1992
[6] Ibid, no. iii
[7] Solchanyk, R., Ukraine and Russia: The Post-Soviet Transition. Rowman and Littlefield Publishers. 2000.
[8] Goldgeier, J. and Michael McFaul. “Power and Purpose: U.S. Policy Toward Russia after the Cold War”, Brookings Institution Press, 2003
[9] Ibid, no. iii
[10] The comment was made by Gleb Pavlovskii, a Russian Political Scientist. quoted in Ben Judah (2013), Fragile Empire: How Russia Fell In and Out of Love with Vladimir Putin. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, p. 85.
[11] Ibid, no. iii
[12] Wigell, M. and A. Vihma, Geopolitics versus geoeconomics: the case of Russia’s geostrategy and its effects on the EU. International Affairs, 92: 605-627. May 6, 2016
[13] Ibid, no. iii
[14] Harper, J. (2021, December 23). Nord stream 2: Who wins, who loses? Deutsche Welle. https://www.dw.com/en/nord-stream-2-who-wins-who-loses/a-60223801
[15] Ukraine: Nord stream 2 a ‘dangerous geopolitical weapon’. (2021, August 22). DW.COM. https://www.dw.com/en/ukraine-nord-stream-2-a-dangerous-geopolitical-weapon/a-58950076
[16] Pifer, S. “Nord Stream 2: Background, Objectives and Possible Outcomes”, Brookings, April 2021 https://www.brookings.edu/research/nord-stream-2-background-objections-and-possible-outcomes/
[17] WikiLeaks. (2008, August 14). UKRAINE, MAP, AND THE GEORGIA-RUSSIA CONFLICT, Canonical ID:08USNATO290_a. https://wikileaks.org/plusd/cables/08USNATO290_a.html
[18] Gardner, F. (2022, March 21). Mariupol: Why Mariupol is so important to Russia’s plan. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-60825226
[19] Blank, S. (2018, November 6). Why is the Sea of Azov so important? Atlantic Council. https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/ukrainealert/why-is-the-sea-of-azov-so-important/
Featured Image Credits: Financial Times
[powerkit_button size=”lg” style=”info” block=”true” url=”https://admin.thepeninsula.org.in/2022/03/29/tpf-analysis-series-on-russia-ukraine-conflict/” target=”_blank” nofollow=”false”]
TPF Analysis Series on Russia – Ukraine Conflict #1
[/powerkit_button]

[powerkit_button size=”lg” style=”info” block=”true” url=”https://admin.thepeninsula.org.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Policy-Brief-NEP-2020.docx-1_compressed-1.pdf” target=”_blank” nofollow=”false”]
Download – Policy Brief on National Education Policy, 2020
[/powerkit_button]
Executive Summary:
In line with the New Education Policy (NEP) 2020 mandate, the UGC released the draft National Higher Educational Qualifications Framework (NHEQF) in February 2022. Its release has reignited the controversy over the policy that was criticized and even rejected by many state governments. The inclusion of Education in the concurrent list gives overriding powers to the centre. However, the sweeping changes the NEP is set to bring have raised concerns that the states would turn into mere implementing agencies while all the decisions regarding education will be taken by the centre. At the root of the controversy lies the federal structure of India which would be jeopardized by the implementation of the policy. Hence, significant and appropriate amendments to the draft are required to address the grievances of the states.
What is NEP (2020)?
The NEP, released in July of 2020 by the Union Government, seeks to overhaul the entire education system of the country by replacing the thirty four-year-old National Policy on Education (1986). In the domain of pre-University education, the new policy aims to transform the curricula structure from 10+2 to 5+3+3+4, mandates the Three Language Formula (TLF), reduces the syllabus to make board exams “easier” and gives thrust to vocational training and skill development. In the realm of higher education, it envisions a single regulator- the Higher Education Council India (HECI)- for Higher Education Institutes (HEIs) by merging UGC, AICTE and other regulatory bodies. The HECI is further divided into four verticals, namely the National Higher Education Regulatory Council (NHERC), National Accreditation Council (NAC), Higher Education Grants Council (HEGI) and General Education Council (GEC).
The policy introduces four-year undergraduate programmes with multiple exit options, along with proposing a national Academic Bank of Credit and a national entrance exam for all universities. It further allows higher education to be taught in regional languages. Additionally, it proposes the National Testing Agency (NTA) conduct a “high quality” common entrance test and a common specialized subject exam in sciences, humanities, language, arts, and vocational subjects, at least twice a year. It blurs the distinction between research-oriented and employment-oriented education, emphasizing a multidisciplinary approach to education. Additionally, it proposes facilitation to top global universities to set up campuses in India and to top Indian Universities to establish campuses abroad.
The policy also touches upon the issue of Adult Education. It proposes strong and innovative government initiatives to achieve 100% adult literacy, educate about critical life skills (including financial literacy, digital literacy, commercial skills, health care and awareness etc.), impart vocational skills and provide basic education to adults. It also ensures providing the necessary infrastructure for adults to facilitate its implementation.
Why is it a problem?
Since its release, the policy has been opposed by a few states. Though other states have voiced their reservations, none have been as vocal and vehement as Tamil Nadu.
The Three Language Formula finds its explicit mention in Section 4.13 of the Draft policy. In order to promote multilingualism, the draft states that, “The three-language formula will continue to be implemented”. Moreover, a student is given the option to change one of the three languages only once- in Grade 6 or 7. Though the formula has been in continuance since the 1970s, an exclusive emphasis upon it raises eyebrows. The draft further falls short of assuring the states unwilling to implement the formula of any compulsion by the centre, instead offering “greater flexibility” in its implementation.
Learning Hindi has always been a controversial issue in Tamil Nadu. The state has seen numerous instances of violence and public protests against the imposition of Hindi. The state has also actively promoted Tamil learning in schools. In 2006, the state enacted Tamil Nadu Tamil Learning Act, making it compulsory for every school operating in the state to teach Tamil. The state government is also opposed to the establishment of Navodaya Schools by the centre in the state.
Laying such a huge emphasis upon an archaic language in schools and even HEIs at “all levels” would leave a student burdened with an unnecessary curriculum. Offering courses in Sanskrit to college students, for instance, in non-Hindi speaking states would decrease their grades. Worse still, in Central Universities- mostly dominated by Hindi speakers, such courses will make naked and even exacerbate the language barrier the non-Hindi speaking students face. Further, the postulate that most of the major Indian languages owe their “origins” to Sanskrit is not even remotely true. Additionally, the literature in Sanskrit can be discriminatory against varna, caste or group, especially in social sciences.
Owing to its vague language, the draft lacks clarity on the extent of jurisdiction of HECI and its verticals. It reserves the power to regulate the faculty/staff, courses, educational outcomes etc., thus infringing upon the state’s rights on reservations and education. Moreover, the students are required to acquire “specific skills” and “learning outcomes” framed by the central government, making it difficult for them to cater to the needs of their respective states. Further, the vocabulary used, such as “good governance”, leaves room for significant manipulation in the future.
Tamil Nadu’s objection to a country-wide entrance test is premised upon the recommendations of the M. Anandakrishnan committee. Constituted in 2006, it recommended the abolition of the Common Entrance Test (CET) in the state from the academic year 2007-08 (Srinivasan, 2016), due to the unaffordability of the high fees of coaching for the rural and underprivileged students. Furthermore, the NRF is empowered to fund the research on urgent “national” issues, thus again leaving the door ajar for manipulation of their jurisdiction, and depriving state-funded institutions of funding for research on regional issues.
In subjugating the administrative system of the colleges to a central body, the central government ignores the urban-rural divide and caste-based discrimination entrenched in them. Moreover, drafting the same guidelines for urban, rural, minority etc. institutions would, along with waning their autonomy, undermine the purpose they are meant to serve.
The central government does not contemplate the unintended consequences of the above proposition, especially for the backward communities and female students. It leaves the students of the said groups with multiple exit options but few entry options. Multiple choices of exit will compel such students facing monetary or familial issues to quit their education in the middle. Further, it burdens a teenage student with critical life-changing decisions. Moreover, the proposed system disallows a student to carry backlogs into the next year, bringing about the apprehension of exacerbation of the dropout rate, which currently stands at 12.6%.
Tamil Nadu’s response to NEP
Since early on, Tamil Nadu’s policies have emphasized education as a modus operandi to uplift the backward castes. As early as 1919, certain legislations were in place to encourage and mandate local education authorities to establish schools at places that were accessible to everyone, thus broadening the social base of its educated bracket. The reasons for the Tamil Nadu government opposing NEP are manifold.
Tamil Nadu Chief Minister MK Stalin has explicitly stated that the policy will not be implemented in the state. He has called it a policy “for elites” and, if implemented, education “will be confined and limited to a few sections”. The state government has even set up a committee to formulate its own State Education Policy in a bid to replace the NEP. Furthermore, the state plans to implement only some ‘good aspects’ of the central policy (Sathyanarayana, 2021). It claims that the policy negates the efforts of more than a hundred years of social justice aspirations that were carefully envisaged in Tamil Nadu. State Education Minister K. Ponmudi noted that mandating entrance exams for getting admissions to arts and science colleges would affect the students from rural areas.
Similar concerns were raised by L. Jawahar Nesan, head of the All India Save Education Committee, while complaining that the proposed Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) could result in “students dropping out of higher educational institutions before completing their course”. “The proposed system aims at furthering vocational education and creation of a workforce pool”, he added (“Academics call for the withdrawal of draft”, 2022). The State Platform for Common School System- Tamil Nadu (SPCSS-TN) termed the framework “a crude form of diarchy”(Sathyanarayana, 2022). Regarding the mandatory entrance test akin to NEET, PB Prince Gajendra Babu, General Secretary of the body, said that the students don’t have sufficient time and their family circumstances do not permit them to undergo separate coaching for entrance exams(ibid). In September last year, the Coimbatore-based Aram Seiya Virumbu Trust filed a writ petition in Madras High Court challenging the constitutionality of Section 57 of the 42nd Amendment that brought education in the concurrent list as a response to the policy, whose implementation, the trust alleged, will lead to “autonomy of the states in education be completely taken away thereby striking at the very root of the federal structure”(Imranullah S., 2021).
The issue of centralization of education has always been a hot potato in the state. Back in 2006, M. Karunanidhi’s government constituted a committee under the chairmanship of M. Anandakrishnan to recommend measures for the abolition of the Common Entrance Test (CET) in the state from the academic year 2007-08. On the recommendations of the committee, the state government terminated its practice of conducting CET for admission into technical and medical courses, making it easier for underprivileged students to pursue the said graduate courses (Rajasekaran, 2021). Other policy decisions taken by the state for similar causes include the 50% ‘in-service’ super speciality seats quota in government medical colleges which was recently upheld by the Supreme Court. Prior to NEET, the quota had provided opportunities to the lower strata of society to enter the colleges which in turn helped the state government in providing an uninterrupted supply of doctors in primary health centres (P.M., 2019).
Other States’ Response
Among other states, West Bengal has most emphatically opposed the implementation of the policy. Within a month of its release, Partha Chatterjee, the state Education Minister, announced the government’s unwillingness to implement the policy in the state “any time soon”, due to its undermining of the federal structure and non-inclusion of Bengali in the list of classical languages(“No NEP 2020 in West Bengal”, 2020). He also said that no one in the state government was consulted for its formulation. Kerala has also protested against the policy in the report of the six-member committee, chaired by Professor Prabhat Patnaik.
Delhi Education Minister Manish Sisodia accused the central government of encouraging the privatisation of education and reducing its responsibility as a government to provide quality education to all, while questioning the need to make board exams easier. Chhattisgarh CM Bhupesh Baghel termed it as centralization of education which goes against the federal structure of the country(Sharma, 2020). Rajasthan Education Minister Govind Datasra also criticized the draft for lack of clarity.
Conclusion
The policy possesses strong tendencies of centralization of education, contravening federalism as a basic structure of our constitution. It establishes bodies that are empowered to determine policies and curriculum for all educational institutions, including state institutions, with little or no role of the states in formulating them, turning them into mere implementing bodies. Moreover, it imposes teaching of Hindi and Sanskrit in all schools across the country with no consent of the states. The policy violates numerous Supreme Court rulings that have upheld federalism as a basic structure of the constitution. The central government must make significant changes to the draft policy to make it more reflective, just and fair to India’s diversity.
Recommendations
References
Featured Image: Deloitte
[powerkit_button size=”lg” style=”info” block=”true” url=”https://admin.thepeninsula.org.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Policy-Brief-NEP-2020.docx-1_compressed-1.pdf” target=”_blank” nofollow=”false”]
Download – Policy Brief on National Education Policy, 2020
[/powerkit_button]

The Peninsula Foundation is releasing a series of analysis papers on the Ukraine-Russia conflict to help the public have a better understanding of the geo-political and security dimensions underlying the conflict. The first paper of the series will introduce you to an overview of the historical, political and humanitarian aspects of the ongoing conflict which is snowballing to be a major conflict and a turning point in Europe’s history since World War II.
Russia – Ukraine History
Russia and Ukraine have had a long interwoven history, since as early as the 18th century. One of the most contested territories, Crimea, was first annexed by the Russian empire in 1783 back when it was controlled by the Crimean Khanate. The territory then became a part of the erstwhile Soviet Union in 1921, to be later controlled by Nazi Germany for a brief period in 1942. Following the end of World War II, the autonomous status of Crimea was dissolved as it now became a province of the USSR, but was later handed over to Ukraine as a goodwill gesture by Nikita Khrushchev in 1954 to mark the 300th anniversary of Ukraine’s reunification with the USSR.

Crimea: White Russian refugees gathering at a Crimean port during the Russian Civil War.
Image: Library of Congress, Washington, D.C.
With the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, many had expected Boris Yelsten to take up the issue and bring back Crimea to Russia, but instead, the Crimean parliament proclaimed the independence of its territory in May 1992, a proclamation only to be annulled by Ukraine. Over twenty years later, a similar referendum, with most of the Crimean population voting to join Russia – a referendum declared illegal by Ukrainian and European governments alike. What followed next was a dramatic escalation with the deployment of the Russian Black Sea Fleet.
Some have argued that NATO’s expansion towards the East is the primary cause of the war, since the organisation was formed primarily to counter the Soviet Union during the Cold War. While it must be acknowledged that such expansion was to be viewed by Russian officials as a provocation even back in the 1990s, the arguments, however, also take away the agency of states in Eastern Europe with most of them ‘demanding’ to join NATO, eager to reap the benefits of the West’s economic system. Over the years, several small states, including Georgia, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Azerbaijan and Moldova, have seen their relationship with the West as a tool to bring regional stability, and increase their bargaining power against Russia.

Events leading up to the war
2021 was a year of security challenges that shook the world amid an ever-mutating Covid-19 pandemic. In October 2021, Russia started moving its troops and military equipment closer to the Ukraine border rekindling concerns of a potential invasion. By mid-December 2021, Russia’s Foreign Minister, Sergey Lavrov released a set of security guarantees and assurances to be met by the U.S. and NATO in exchange for non-intervention in Ukraine. Putin also threatened unspecified ‘military technical’ measures if the West fails to accede to his demands. Putin’s major demands were; (i) Ban on Ukraine entering NATO, (ii) No further expansion of NATO in the Eastern European region, (iii) Withdrawal of any troops or weapons deployed in countries which entered NATO after 1997 (Poland, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, and the Balkan countries), (iv) No NATO drills to be conducted in Ukraine, Georgia and Central Asia without prior agreement with Russia. Although NATO was formed to counter the USSR during the Cold War, it continued its expansion into Eastern Europe territories even long after the dissolution of the USSR. Putin was threatened by the continuous NATO expansionism, the security implications and the loss of the Russian sphere of influence in Eastern Europe.
The U.S. and NATO immediately rejected these main demands warning if Russia invades Ukraine, there will be serious retaliation and Russia will be met with a ‘massive forceful package’ of economic sanctions. Ukraine’s Foreign Minister Kuleba had said that although they were expecting and already experiencing aggressive Russian cyber-attacks and destabilisation of the Ukrainian economy, the number of Russian troops on the border was ‘insufficient’ and the build-up was missing some key military indicators to execute an imminent ‘full-scale invasion’ of Ukraine. Many experts and theorists also opined that despite Putin’s bold demands and his game of brinkmanship, the reality of war was in question.
On 21st February, in a televised address Putin said that ‘Ukraine is an integral part of Russia’s history’ and declared the regions of Donetsk and Luhansk as independent Republic States and sent Russian troops into those regions for ‘peacekeeping’.
The beginning of February showed some positive signs of diplomacy or at the least maintenance of the status quo between Ukraine and Russia despite the West’s declining Putin’s demands. However, it was only calm before the storm. On 21st February, in a televised address Putin said that ‘Ukraine is an integral part of Russia’s history’ and declared the regions of Donetsk and Luhansk as independent Republic States and sent Russian troops into those regions for ‘peacekeeping’. As a response to this, the US and other NATO members imposed economic sanctions on Russian parliament members, banks and other assets and Germany decisively halted the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline project.
‘Special Military Operation’

On 24th February, Putin announced a ’special military operation’ and Russian forces launched missile and artillery attacks on major Ukrainian cities including Kyiv. Ukrainian Foreign Minister affirmed that Russia has launched a ‘full-scale invasion of Ukraine’, following which Ukraine shut down its entire airspace as a response to the Russian operation in Donbas. The West imposed further sanctions on Russia including but not limited to, removing select Russian banks from the SWIFT system, freezing the assets of the Russian Central Bank and curbing products exported to Russia.
Zaporizhzhia is a vital asset in fulfilling Ukraine’s energy requirements with six nuclear reactors with a capacity of generating 950MW per reactor. Capturing Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant would have been a major plan of the invading forces given its strategic nature.
Nearly four weeks since the Russian Federation launched a ‘special military operation’, the situation on the ground in Ukraine continues to remain dire. The United Nations Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine (HRMMU) has been responsible for documenting civilian casualties in Ukraine since 2014. In the span of three weeks, Ukraine’s infrastructure and cultural heritage have suffered irreparable damage or been completely destroyed. The ceaseless shelling by Russian forces of cities and hospitals have exacerbated the human toll.
According to a press briefing released by the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), civilian casualties as of 26 March 2022 stand at 2,909 – 1,119 people killed and 1,790 injured.
The OHCHR assesses that actual figures might be higher than what is currently being reported as they wait for figures to be corroborated. Most of the civilian casualties are reportedly caused by explosive weapons with a wide impact area. This includes shelling from heavy artillery and multiple-launch rocket systems and missile and air strikes.
In a rather unexpected move, on 4th March, 2022 the Russian forces attacked and captured the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant, located in Energodar, Ukraine. Zaporizhzhia is a vital asset in fulfilling Ukraine’s energy requirements with six nuclear reactors with a capacity of generating 950MW per reactor. Capturing Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant would have been a major plan of the invading forces given its strategic nature.
The Russian attack on the nuclear plant raised alarm bells among nations and nuclear watchdogs. Intense shelling on the complex caused a fire in one of the training buildings. Reports have noted the damage to multiple locations within the complex. The Ukrainian government was quick to act and called it an “act of terror”. Contrary to Ukrainian claims, the Russian Ministry of Defence spokesperson Maj. Gen. Igor Konashenkov claimed that the entire event was a sabotage act by the Ukrainian forces. With Chernobyl captured very early in the invasion, the attack on Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant raises questions about the safety and security of nuclear infrastructures during times of crisis.
On March 9, 2022, a hospital in Mariupol that also housed a maternity ward came under attack. It was reported that at least 4 people were killed in the bombing, including a pregnant woman. Presently, Mariupol is seeing some of the fiercest attacks, since the port city is a strategic target for Russia. It is estimated that some 300,000 people are trapped with supplies running low. The Russian Federation’s offer of safe passage out of Mariupol for the Ukrainian people has been summarily rejected by Ukraine’s Deputy Prime Minister Iryna Vereshchuk who was quoted saying, “There can be no question of any surrender, laying down of arms”.
Other areas to have been hit include Kyiv, Kharkiv, Borodyanka, Ochakiv, Sumy, Mykolaiv, Odessa etc. On March 1, the Central Freedom Square in Kharkiv was bombed that leaving both the administrative building and surrounding structures destroyed. On 14 March the Ukrainian health minister Viktor Liashko reported that nearly 100 hospitals had been damaged. As of 17 March, the World Health Organisation (WHO) has verified 44 instances of attacks on healthcare facilities in Ukraine.
West’s Sanctions
The global media coverage of the invasion can be best described as a cacophony of partisanship. The western media has been charged with accusations of brushing off Russian security concerns and, of course, brazen racism. It has followed its own orientalist approach to present the crisis as a result of Russian imperialism.
The West has swiftly responded by imposing sanctions; a course of action meant to deter and halt Russia’s actions in Ukraine. Germany’s Chancellor Olaf Scholz announced halting final approval for the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline following Russia’s recognition of two breakaway regions of Eastern Ukraine – Luhansk and Donetsk.
On 8 March, President Biden, with bipartisan support, announced that the US would be banning imports of Russian oil, gas and energy. The UK also announced that it would phase out Russian oil imports by the end of 2022 on the same day. Both the US and the UK are working with their European counterparts to reduce dependency on Russian hydrocarbon imports. The European Commission responded to Russia’s aggression in Ukraine by stating that the EU countries would work to become independent of Russian energy imports “well before 2030”. Other economic deterrents imposed have been the ban on exports of luxury goods like vehicles, fashion and art to Russia by the UK and EU. The UK has also imposed a 35% tax on imports from Russia, including vodka. Russian oligarchs’ assets in the US, UK and the EU have been targeted. Sanctions have also been imposed on former Russian leaders, ministers and current members of the Russian Parliament.
Russian flights and private jets have been banned from the US, UK, EU and Canadian airspaces. The G7 countries have also stripped Russia of its “most favoured nation” status; a move that will impact Russia’s trade. Assets of most Russian banks have been frozen and some of them have been removed from the international financial system SWIFT. Other countries to have imposed sanctions on Russia include Japan, Taiwan, New Zealand, Australia and Switzerland. Australia moved to ban exports of alumina and aluminium ore, including bauxite to Russia. Russia relies on Australia for 20% of its alumina requirements – aluminium being a major export for Russia. Several energy, automobile, tech, financial, food and fashion companies have also halted operations in Russia – Exxon, Shell, Apple, Alphabet, Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, Ferrari, Harley-Davidson, Nike, McDonald’s etc.
Globally, the impact of the Russia-Ukraine war has been felt in oil markets as prices continue to surge to well over $100 per barrel. Russia’s response to being hit with global sanctions has been to ban the exports of over 200 products, including telecoms, electrical equipment, agricultural, medical goods etc. However, this list does not include energy and raw material resources. It has also banned and blocked interest payments to foreign investors and dividends to overseas shareholders and also banned the sale of Russian stocks and bonds held by foreign investors. It has also passed a decree suspending the IP rights of ‘unfriendly countries’.
On 15 March, President Zelensky said that it must be accepted that Ukraine will not become a member of NATO, possibly appeasing one of Putin’s major security concerns. Additionally, on 15 March, Moscow announced its decision to withdraw from the Council of Europe after 26 years of membership, hours ahead of a formal decision taken by the Council to expel Russia over its aggression in Ukraine. The move also means that Russia will no longer be a signatory to the European Convention on Human Rights, depriving its citizens of the right to appeal to the European Court of Human Rights. A statement from the Russian foreign ministry cited that the EU and NATO had “destroyed” the Council of Europe and turned the organisation into an “anti-Russia policy tool”.
Russia also made the decision to sanction President Biden, Prime Minister Trudeau and several top US officials. The list includes Secretary of State Anthony Blinken, Defence Secretary Lloyd Austin, National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan, CIA Director William Burns, WH Press Secretary Jen Psaki and former Secretary of State and Democratic Presidential candidate Hilary Clinton.
The global media coverage of the invasion can be best described as a cacophony of partisanship. The western media has been charged with accusations of brushing off Russian security concerns and, of course, brazen racism. It has followed its own orientalist approach to present the crisis as a result of Russian imperialism. Popular Russian media channels such as RT and Sputnik have been banned by YouTube across Europe, essentially leading to the West dominating the information warfare, controlling the narrative and presenting a one-sided perspective to the world. The Russian Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Media, commonly known as the Roskomnadzor, released a statement informing media and other information sources that any publication regarding the ‘special military operation’ must only use the information received from Russian officials. Several independent Russian media outlets like Ekho Moskvy, InoSMI, Mediazona, New Times, Dozhd, Svobodnaya Pressa, Krym, Realii, Novaya Gazeta, Journalist, Lenizdat etc. were sent notifications by the Roskomnadzor on allegations of reporting false information regarding the actions of the Russian Army, shelling in Ukrainian cities and referring to the military operation as ‘war’, ‘invasion’ and ‘attack’. Nonetheless, some media houses have stood up to the pressure to report more appropriately.
The war in Ukraine could also leave lasting environmental damage, being a highly industrialised state. The threat of radiation resulting from an attack on any one of Ukraine’s nuclear plants could have devastating consequences. Carcinogenic dust from bombed buildings, groundwater contaminations from spilled chemicals and attacks on industrial facilities will have a lasting impact on the health of the people in the country.
UN Response
As Russian troops continue to shell Ukrainian cities, the various United Nations bodies have called for emergency meetings, albeit with no successful outcome to halt the war. In February 2022, a Security Council meeting calling for a resolution to condemn the Russian military operations and demanding an end to Russian attacks had similarly failed with the resolution having been vetoed by Russia.
Although Putin’s end may not justify his means, one needs to look at this crisis holistically and historically. Putin may have been the one to declare war, but the triggering and contributing events and actions by NATO and the US should also be taken into consideration while analysing this conflict.
However, the United Nations has been swift with its humanitarian response, an effort visible with its coordinated appeals calling for the allocation of an estimated USD 1.7 billion to help the Ukrainians. Dividing the allocation of funds into two categories – one for people within Ukraine, and the other for its comprehensive response towards refugees coming from Ukraine, the United Nations’ relief efforts have seen one of the most generous responses to its funding appeal. Further, as fighting continues amidst multiple rounds of talks between Russia and Ukraine, UN Agencies, including UNICEF, continue to supply humanitarian aid, including medical supplies to the country. As part of its cash-response strategy, the UN agencies have additionally planned to implement its program of cash-for-rent assistance, where they seek to provide the affected population with the resources to find themselves an accommodation, in order to avoid large-scale displacement.

Although Putin’s end may not justify his means, one needs to look at this crisis holistically and historically. Putin may have been the one to declare war, but the triggering and contributing events and actions by NATO and the US should also be taken into consideration while analysing this conflict. It seems to be that Putin has not entered into an all-out war yet, as his objectives and weaponry employed are limited. In the forthcoming series of analyses, The Peninsula Foundation delves into each of the facets of the conflict mentioned in this paper.
Featured Image Credits: The Times
NATO Expansion Image Credits: Statista
Russian General Image Credits: Moscow Times
UNSC Image Credits: Harvard Law Today

[powerkit_button size=”lg” style=”info” block=”true” url=”https://admin.thepeninsula.org.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Change-in-IAS-Cadre-Rules-1.pdf” target=”_blank” nofollow=”false”]
Download – Change in IAS (Cadre) Rules
[/powerkit_button]
Executive Summary:
The Centre’s proposal to amend the IAS Cadre Rules has sent shockwaves through the State governments and the bureaucratic community. Although the Centre already has the preponderance of power over the State government, it has always been the convention to depute All India Services (AIS) officers with the concurrence of the State government(s) and the Central government and the consent of the officer concerned. By providing overriding powers to the Central government, the proposal poses a fundamental risk to the federal structure of the Constitution. Not only should the proposal be recalled, but the annual intake of the IAS officers should be increased to address the issue of staff shortage, while recruiting suitable personnel from other Central Civil Services. The empanelment process also needs to be reformed to ensure transparency, objectivity and to uphold the principles of natural justice.
The Centre’s proposal is a reflection of the long overdue need for the complete overhaul and reform of the Indian civil service system. These piecemeal amendments and a myriad of executive orders are not only unproductive to the civil service system but also counterproductive to the basic structure of the Constitution. A high-level committee should be established to undertake a holistic study to reform the Indian civil service system not only to bring in better performance and accountability but more importantly, to get rid of the colonial legacy once and for all.
What is it?
Deputation of IAS officers is governed under Rule 6 of The Indian Administrative Service (Cadre) Rules, 1954. Rule 6(1) mandates that the deputation of cadre officers to the Centre must be done with the concurrence of the concerned State government(s) and the Central government.
The provision to Rule 6(1) states that in case of any disagreement, the Central government’s decision will prevail, and the State governments shall give effect to it.
The proposal attempts to amend the Central Deputation rules by giving overriding powers to the Centre to transfer and post Cadre officers without the consent of the State government.
Proposed Amendments (Singh, 2022)
1. ‘Within a specified time’
The proposal amends the proviso mandating the State governments to give effect to the final decision of the Central government within a specified time as decided by the Central government.
2. ‘Officer shall stand relieved’
In case, a State government delays a cadre officer’s deputation to the Centre and does not give effect to the Central government’s decision within a specified time, the concerned ‘officer shall stand relieved from the cadre from the date as may be specified by the Central government’.
3. ‘Number of officers’
Another change proposed is that the actual number of officers to be deputed to the Centre shall be decided by the Central government in consultation with the State government which is required to provide a list of eligible names.
4. ‘Public interest’
In a specific situation, if the need arises for the services of a cadre officer to be utilized by the Central government in the public interest, the State governments shall give effect to it within a specified time.
The abovementioned amendments were sent to the State governments in a letter dated 12th January 2022 by the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) seeking comments until 25th January. The DoPT had earlier sent three similar letters (dated 20th,27th December and 6th January) which were strongly opposed by six States (including BJP ruled States) (Singh, 2022). As of now, more than 7 States have written to the DoPT opposing the proposed changes and other states such as Maharashtra, Kerala and Tamil Nadu have also raised their opposition. The CMs of Chhattisgarh and Rajasthan have also written to the PM opposing the proposed amendments to the cadre rules.
Why is it a problem?
The proposed amendments are essentially an attack on the federal structure of our Constitution since it derogates the State government’s power in posting and transferring its cadre officers without its consent. In spite of the rules giving preponderance of power to the Centre, it has always been the convention to depute officers to the Centre in concurrence with the State governments and the consent of the officer concerned (Dhingra, 2021).
Mamata Banerjee, the CM of West Bengal wrote a strongly worded letter to the PM opposing this move and calling it a ‘unilateral decision’ which was ‘historically unprecedented and wholly unconstitutional’.
The trigger for this move by the Centre is most likely the result of the tussle between the Centre and West Bengal over former IAS officer Mr. Alapan Bandhopadhyay. Given his experience in handling the Covid-19 crisis as the Chief Secretary of West Bengal, the State government had requested the Centre to extend his tenure and the latter acceded by extending his term for 3 months (24th May 2021). However, the Centre on 28th May 2021 did a complete 180° and issued an order to Mr. Bandhopadhyay informing him that he has been placed with the Government of India ‘with immediate effect’. Following this, the State government opposed the order and did not relieve him and the concerned officer also opted to retire from the services and is now appointed as the advisor to the CM. The Centre then issued a show-cause notice to Mr. Bandhopadhyay for his failure to report to the DoPT. There have been other similar tussles in the past between the Centre and Tamil Nadu government (2001) and West Bengal government (2020) (Agnihotri, 2021), but when the States refused to relieve the concerned IPS officers, the Centre upheld the convention of State government concurrence and did not insist on deputing them anyway.
Shortage of officers in the Centre
The DoPT cites the shortage of AIS officers in Union Ministries as the driving factor for these proposed amendments since the ‘States are not sponsoring an adequate number of officers for Central Deputation’. While this is true, it is pertinent to note that State governments also have been suffering from a shortage of officers, especially during the pandemic and have requested the DoPT multiple times to increase the cadre strength of IAS officers (West Bengal, Rajasthan, Bihar).
Senior IPS officers advise that the problem of shortage of AIS officers has been perennial and does not warrant a knee-jerk reaction at the cost of violating the basic structure of our Constitution. The problem of shortage must be seen as secondary to upholding the federal structure especially since there are other ways to address this problem without seizing the State governments’ authority. While only AIS officers come under the common purview of both the Central and State governments, there are other Central Services with ample human resources over which the Central government has sole authority and the shortage can be filled by deputing these Central services officers.
The Empanelment Process
The empanelment process of AIS officers in India has been infested with executive arbitrariness and a lack of transparency. The procedure for empanelment is laid down in the Central Staffing Scheme which does not have any legislative sanction and is instead governed by a slew of Executive Orders (E.O), the primary dated 5th Jan 1996 (NO.36/77/94-EO(SM-I)). The flawed Annual Confidential Report system was replaced by the Annual Performance Appraisal Reports (APAR) system following a Supreme Court ruling to ensure more transparency.
However, the additional layer of review with the 360° appraisal system or the Multi-Source Feedback system introduced by PM Modi in April 2015 allows the panel to override the recommendations of the APAR system.
The 92nd Report of the Department-Related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice in 2017
reprimanded the 360° system for its opacity and lack of objectivity, thereby leaving the empanelment process ‘susceptible to manipulation’. Former Upper-level Secretaries have also been critical about the 360° system due to its
▪ Lack of transparency
▪ Absence of an appeal process
▪ Susceptible to bias and discrimination.
(MS, 2018)
The absence of legal backing for the empanelment procedure has led to the arbitrary exercise of power by the executive. Usually, officers start their career after training in State cadres and it would take up to 9 years for an officer to occupy Central government positions. But the present government has started a practice of appointing newly recruited officers, fresh from training, as Assistant Secretaries in the Union Ministries. Although this move was said to increase exposure for the new officers, it also may as easily be detrimental to their careers. This new pattern, initiated by the Modi govt, is characterised by a lack of transparency and establishing a core group of loyalist officers at the cost of building experience, knowledge, and performance. The loyalty of the officers of the civil services must be to the Constitution alone and not to any political party or even government of the day if it violates the constitutional provisions.
Already, the AIS officers are in a bind where the State government and Central government are governed by opposing parties. The lack of fairness in the empanelment process has further discouraged and disheartened officers from Central Deputation. Although salaries and incentives remain the same, the State governments use transfers and postings as de facto punishment for AIS officers who do not follow suit with the State government’s decisions. Similarly, the Central government beguiles AIS officers with the temptation of post-retirement postings. The proposed amendments grant overreaching powers to the Central government which could be used to harass and corrupt an
unwilling officer.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the proposed amendments derogate the consent of State governments and the officer concerned. This not only gives rise to a lack of transparency and increased bias, but also has the potential to disintegrate the delicate federal structure that has been upheld since Independence. The Supreme Court has on many occasions emphasized that federalism is a part of the basic structure of our Constitution, and even a Constitutional amendment cannot do away with it. The Supreme Court has also affirmed cooperative federalism as a ‘cherished Constitutional goal’. Therefore, the Central government must look at other ways to overcome the issue of staff shortage, without granting itself overarching powers in direct violation of the Constitution.
Recommendations:
▪ Recall the proposal amending the IAS (Cadre) Rules which will fundamentally damage India’s federal structure, thereby undermining national integrity and security.
▪ Shortage of officers can be addressed, in the short term, by recruiting suitable personnel from other Central Services such as IRS, Indian Defence Accounts service, Customs, etc. Alternatively, well-known professional experts in various fields can be inducted at senior positions, which will not only address the shortage but also the need for professional competence and experience in specialist departments as against the oft raised complaint of generalist nature of the IAS.
▪ Keeping in mind the demands of the Covid-19 pandemic, increase the annual intake of IAS officers to address the shortfall of 22 per cent in IAS posts.
▪ Increase Lateral recruitment for Central posts on a contract basis in the short term.
▪ The empanelment process, especially the 360° Appraisal system must be completely reformed to ensure equal opportunity and better transparency.
▪ The Centre’s proposal is a reflection of the long overdue need for the complete overhaul and reform of the Indian civil service system. These piecemeal amendments and a myriad of executive orders are not only unproductive to the civil service system but also counterproductive to the basic structure of the Constitution. A high-level committee should be established to undertake a holistic study to reform the Indian civil service system not only to bring in better performance and accountability but more importantly, to get rid of the colonial legacy once and for all.
References:
1. Agnihotri, S. (2021, June 4). Centre’s tussle with Bengal over chief secretary Reeks of uncooperative federalism. The Wire. Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://thewire.in/politics/centres-tusslewith-bengal-over-chief-secretary-reeks-of-uncooperative-federalism
2. Dev Dutt v. Union of India & Ors., (2008) 8 SCC 725
3. Dhingra, S. (2021, June 7). Centre vs states, rules vs convention – who really controls IAS officers. ThePrint. Retrieved January 26, 2022, from https://theprint.in/india/governance/centre-vs-statesrules-vs-convention-who-really-controls-ias-officers/672013/
4. Mishra, N. (2021, June 7). Explained: Chief secretary appointment controversy. TheLeaflet. Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://www.theleaflet.in/explained-chief-secretary-appointmentcontroversy/
5. MS, N. (2018, August 29). Why India’s civil servants are disaffected with the 360-degree empanelment process for top central government posts. The Caravan. Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://caravanmagazine.in/government-policy/why-indias-civil-servants-disaffected-with-360-degree-empanelment
6. Rajya Sabha, 92nd Report, Appraisal and Empanelment of Civil Servants under the Central Government, Department-Related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice, August 2017, available at http://164.100.47.5/newcommittee/reports/EnglishCommittees/Committee%20on%20Personnel,%20PublicGrievances,%20Law%20and%20Justice/92.pdf
7. Saxena, N. C. (2022, January 24). Who should control where IAS officers serve? The Wire. Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://thewire.in/government/who-should-control-where-ias-officers-serve
8. Singh, V. (2022, January 20). States weigh options on IAS cadre rule changes. The Hindu. Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/states-weigh-options-on-iascadre-rule-changes/article38293886.ece
9. The Quint, Centre proposes new IAS Cadre Rules: What are they? why are they being opposed? (2022, January 21). Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://www.thequint.com/news/india/ias-cadrerules-mamata-banerjee-narendra-modi-centre-states#read-more
10. Yadav, S. (2022, January 22). Explained: IAS officers and central posting. The Indian Express. Retrieved January 25, 2022, from https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/ias-cadre-rules-amendmentswest-bengal-explained-7734310/
Featured Image: Press Information Bureau (PIB)
[powerkit_button size=”lg” style=”info” block=”true” url=”https://admin.thepeninsula.org.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Change-in-IAS-Cadre-Rules-1.pdf” target=”_blank” nofollow=”false”]
Download – Change in IAS (Cadre) Rules
[/powerkit_button]

Much of the globalized world is experiencing a standstill due to the COVID-19 Pandemic Crisis. While world leaders are establishing measures to cope with the large scale outbreak, technology has been in the forefront as a crucial aspect of recovery. From sanitizer drones to virtual workspaces — the adoption of computing technology in healthcare, businesses and governance has seen an unprecedented rise.
However, due to India’s unique factors of dense population and per capita poverty — the country’s response to this crisis will be an important case study. The World Health Organization’s guidelines insist that people should wash their hands regularly but over 163 million people residing in India do not have access to clean water. When access to fundamental resources are limited, one can only assume that access to robust healthcare facilities are also limited. The stark contrast in the capacity to handle this crisis will be tested when the local communication of COVID-19 reaches the second and third tier cities. As a primary effort in flattening the curve, the government has announced a 21 day country-wide lockdown. In spite of the measure being welcomed, if the country fails to control the spread, the lack of modern infrastructure and medical professionals will result in catastrophic consequences.
This is reflected in the adoption of technology in primary healthcare centres. Medical professionals say there is a shortage of around 70,000 ventilators and the existing resources are being utilized by critical at-risk patients. The surging requirement of intensive care medical devices, including ventilators and high-end diagnostic and robotic surgery instruments is a growing concern. While domestic manufacturing and innovation have been scarce, Indian companies like Skanray Technologies are struggling to meet the immediate demand due to the international airline ban. Companies find it difficult to import crucial equipment such as chips, controllers and sensors from China — hindering their ability to produce these equipment on time.
Globally, innovative technologies that seemed gimmicky in the past are being brought into mainstream practice. Drones have been deployed to carry medical samples and to spray disinfectants across the country. Robots are put in hospitals which aid in remote diagnosing and thermal sensing of the patients. The same is also used as service bots that bring food and toiletries to people.
Facial recognition cameras are commonplace in China and a growing trend in other countries. Technology companies like SenseTime have built contactless temperature detection software that have been integrated into the cameras for wider coverage of people with fever. Big data analytics being done on these massive feeds has resulted in prediction algorithms which can determine whether a person has come in contact with another infected person. This data is then relayed via telecom companies to inform the individuals to self-quarantine.
Complex surveillance systems come with their share of privacy concerns. While the lines between responsible surveillance and invasion of privacy become blurred, one cannot overlook the fact that some of these drastic measures are working. In China, the official reports indicate that the domestic cases are under control and newer cases of the virus are classified as imported. In a time of crisis, an open-minded analysis of these “draconian” measures would seem justified. However, this pandemic has not provided any justification of collecting these sensitive data in secrecy.
Flawless implementation of such systems in India would have to hurdle through multiple policy hoops and comprehensive definitions of data privacy. However, inexpensive technologies such as drones and robotics should spark interest in the country. Medical professionals at the forefront of this battle could benefit from such technology that can reduce their risk of contracting the virus. Alongside technology, modern day practices of preliminary diagnoses such as telemedicine should be encouraged.
Information and communication technologies across the country have made this battle a lighter burden than what it could have been. While the rate of awareness is significantly higher in the age of social media, it is important to note its duality. Online medical information and guidelines are accessible by at least 34% of the total population compared to the 7.5% in 2010. However, this information influx has also resulted in rumour mongering and exaggeration of outlier incidents — causing trivial worry and needless panic. In the past five years, rapid penetration of the internet has occurred in all sections of society but it has not ensured awareness in responsible use of the technology.
On the other hand, the quarantined lifestyle has increased the need for virtual workspace. Facebook’s CEO, Mark Zuckerberg reported that traffic for their video streaming and messaging platform had grown multifold. Microsoft also reported a 40% increase in their active user base of collaboration software. High speed fiber internet’s extension throughout India will help in fragmenting this dense working population to multiple locations. With virology experts anticipating an effective vaccine at the earliest of 18 months — some of these altered lifestyles could become the new norm.
Years following the second world war, measures were actively put in place to prevent another global conflict. The COVID-19 Crisis could leave a similar impact on the world where pandemic response and technology experience drastic reforms. However, the lens of India should vision this wake up call towards something more fundamental — uniformity in primary healthcare, civic infrastructure and technology intervention.
Views expressed are author’s own.

A formal interactive session on Maritime Security was organized in The Peninsula Foundation (TPF), Chennai on September 11, 2019 in collaboration with the United States Consulate, Chennai. The Consulate facilitated the visit of Mr Geoffrey Wessels, Officer for Trade and Connectivity, US Embassy, New Delhi. He was accompanied by Ms Sara Greengrass, Economic Officer, US Consulate, Chennai and Mr George Mathew, Economic Specialist, US Consulate, Chennai. The meeting was aimed to gather perspectives on security challenges faced in the Indo-Pacific region.
Various recent geopolitical developments relating to maritime security, especially in the Indian Ocean Region, were discussed. Development of India’s relations with ASEAN countries and New Delhi’s need to ensure safety in the sea were explored. There was consensus on the concerns against China’s consistent rise in the Asia Pacific and its practice of debt-trap strategy, as in Sri Lanka, while implementing its ambitious One Belt – One Road project across Asia, and the need for India’s maritime security to be prioritized. Ms Sara stressed on environment security in the Indian Ocean due to overfishing and initiatives of USA to minimize maritime non-conventional threats to India. Primarily, the discussion aimed at finding a common ground between India and the US to deal with China. Representatives of TPF elaborated about their perspectives on Beijing and commented on possible collaboration between India and the USA. The session was informative and fruitful; we thank the US consulate for the arrangement and encourage such interactions in the future.
[sc name=”donte”]